General audience texts
Besides the scholarly publications listed below, I have written many texts in English and German. My more notable German texts appeared by DNIP.ch. I also maintain document collections intended for a broad audience:
Scholarly publications
Up-to-date citation counts (provided by Google Scholar). List of patents granted.
2016
Daniel Kaiser; Marcel Waldvogel; Holger Strittmatter; Oliver Haase
User-Friendly, Versatile, and Efficient Multi-Link DNS Service Discovery Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Edge Computing (WEC 2016); in conjunction with IEEE ICDCS 2016, 2016.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: DNS-SD, Multicast, Service Discovery, Zeroconf | Links:
@inproceedings{kaiser2016user-friendly,
title = {User-Friendly, Versatile, and Efficient Multi-Link DNS Service Discovery},
author = {Daniel Kaiser and Marcel Waldvogel and Holger Strittmatter and Oliver Haase
},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/kaiser2016user-friendly.pdf},
year = {2016},
date = {2016-06-27},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Edge Computing (WEC 2016); in conjunction with IEEE ICDCS 2016},
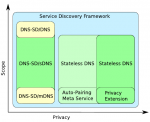
abstract = {When mobile devices at the network edge want to communicate with each other, they too often depend on the availability of faraway resources. Feasible user-friendly service discovery is essential for direct communication. DNS Service Discovery over Multicast DNS (DNS-SD/mDNS) is widely used for configurationless service discovery in local networks; due in no small part to the fact that it is based on the well established DNS, and efficient in small networks.
In our research, we enhance DNS-SD/mDNS providing versatility, user control, efficiency, and privacy, while maintaining the deployment simplicity and backward compatibility. These enhancements are necessary to make it a solid, flexible foundation for device communication in the edge of the Internet.
In this paper, we focus on providing multi-link capabilities and scalable scopes for DNS-SD while being mindful of both user-friendliness and efficiency. We propose DNS-SD over Stateless DNS (DNS-SD/sDNS), a solution that allows configurationless service discovery in arbitrary self-named scopes – largely independent of the physical network layout – by leveraging our Stateless DNS technique and the Raft consensus algorithm.},
keywords = {DNS-SD, Multicast, Service Discovery, Zeroconf},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
In our research, we enhance DNS-SD/mDNS providing versatility, user control, efficiency, and privacy, while maintaining the deployment simplicity and backward compatibility. These enhancements are necessary to make it a solid, flexible foundation for device communication in the edge of the Internet.
In this paper, we focus on providing multi-link capabilities and scalable scopes for DNS-SD while being mindful of both user-friendliness and efficiency. We propose DNS-SD over Stateless DNS (DNS-SD/sDNS), a solution that allows configurationless service discovery in arbitrary self-named scopes – largely independent of the physical network layout – by leveraging our Stateless DNS technique and the Raft consensus algorithm.
2015
Andreas Rain; Daniel Kaiser; Marcel Waldvogel
Realistic, Extensible DNS and mDNS Models for INET/OMNeT++ Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of the “OMNeT++ Community Summit 2015â€, 2015.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: DNS-SD, Mobile Networks, Multicast, Service Discovery, Simulation, Zeroconf | Links:
@inproceedings{rain2015realistic,
title = {Realistic, Extensible DNS and mDNS Models for INET/OMNeT++},
author = {Andreas Rain and Daniel Kaiser and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/rain2015realistic.pdf
https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/rain2015realistic-slides.pdf},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-09-03},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the “OMNeT++ Community Summit 2015â€},
abstract = {The domain name system (DNS) is one of the core services in today’s network structures. In local and ad-hoc networks DNS is often enhanced or replaced by mDNS. As of yet, no simulation models for DNS and mDNS have been developed for INET/OMNeT++. We introduce DNS and mDNS simulation models for OMNeT++, which allow researchers to easily prototype and evaluate extensions for these protocols. In addition, we present models for our own experimental extensions, namely Stateless DNS and Privacy-Enhanced mDNS, that are based on the aforementioned models. Using our models we were able to further improve the efficiency of our protocol extensions.},
keywords = {DNS-SD, Mobile Networks, Multicast, Service Discovery, Simulation, Zeroconf},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2014
Daniel Kaiser; Matthias Fratz; Marcel Waldvogel; Valentin Dietrich; Holger Strittmatter
Stateless DNS Technical Report
University of Konstanz Technical Report, no. KN-2014-DISY-004, 2014.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: DNS-SD, Multicast, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Zeroconf | Links:
@techreport{Kaiser2014Stateless,
title = {Stateless DNS},
author = {Daniel Kaiser and Matthias Fratz and Marcel Waldvogel and Valentin Dietrich and Holger Strittmatter},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/kaiser14stateless.pdf},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-12-31},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {KN-2014-DISY-004},
institution = {University of Konstanz},
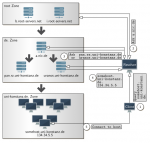
abstract = {Several network applications, like service discovery, file discovery in P2P networks, distributed hash tables, and distributed caches, use or would benefit from distributed key value stores. The Domain Name System (DNS) is a key value store which has a huge infrastructure and is accessible from almost everywhere.
Nevertheless storing information in this database makes it necessary to be authoritative for a domain or to be “registered” with a domain, e.g. via DynDNS, to be allowed to store and update resource records using
nsupdate. Applications like the ones listed above would greatly benefit from a configurationless approach, giving users a much more convenient experience.
In this report we describe a technique we call Stateless DNS, which allows to store data in the cache of the local DNS server. It works without any infrastructure updates; it just needs our very simple, configurationless echo DNS server that can parse special queries containing information desired to be stored, process this information, and generate DNS answers in a way that the DNS cache that was asked the special query will store the desired information. Because all this happens in the authority zone of our echo DNS server, we do not cause cache poisoning. Our tests show that Stateless DNS works with a huge number of public DNS servers.},
type = {Technical Report},
keywords = {DNS-SD, Multicast, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Zeroconf},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
Nevertheless storing information in this database makes it necessary to be authoritative for a domain or to be “registered” with a domain, e.g. via DynDNS, to be allowed to store and update resource records using
nsupdate. Applications like the ones listed above would greatly benefit from a configurationless approach, giving users a much more convenient experience.
In this report we describe a technique we call Stateless DNS, which allows to store data in the cache of the local DNS server. It works without any infrastructure updates; it just needs our very simple, configurationless echo DNS server that can parse special queries containing information desired to be stored, process this information, and generate DNS answers in a way that the DNS cache that was asked the special query will store the desired information. Because all this happens in the authority zone of our echo DNS server, we do not cause cache poisoning. Our tests show that Stateless DNS works with a huge number of public DNS servers.
Daniel Kaiser; Marcel Waldvogel
Adding Privacy to Multicast DNS Service Discovery Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE TrustCom 2014 (IEEE EFINS 2014 workshop), 2014.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: DNS-SD, Multicast, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Service Discovery, Social Networks, Trust, Zeroconf | Links:
@inproceedings{Kaiser2014Adding,
title = {Adding Privacy to Multicast DNS Service Discovery},
author = {Daniel Kaiser and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Kaiser2014Adding.pdf},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-09-24},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE TrustCom 2014 (IEEE EFINS 2014 workshop)},
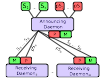
abstract = {Multicast DNS Service Discovery (mDNS-SD), made fashionable through Apple’s \emph{Bonjour}, is a prevalent technique allowing service distribution and discovery in local networks without configuration (Zeroconf). Possible application areas are device synchronization, instant messaging, VoIP, file and screen sharing. It is very convenient for users, because they can connect to and offer services when they enter a network without any manual configuration. However, it requires the public exposure of the offering and requesting identities along with information about the offered and requested services, even when services do not need to be public. Some of the information published by the announcements can be very revealing, including complete lists of family members. In this paper we discuss the privacy problems arising when using mDNS-SD and present our privacy extension, which allows hiding all information published while still not requiring any network configuration except for an initial pairing. A key feature of our solution is the ease of upgrading existing systems, a must for widespread deployment and acceptance. To show the feasibility of our mDNS-SD privacy extension, we developed an implementation based on the open-source \emph{Avahi} daemon.},
keywords = {DNS-SD, Multicast, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Service Discovery, Social Networks, Trust, Zeroconf},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Daniel Kaiser; Marcel Waldvogel
Efficient Privacy Preserving Multicast DNS Service Discovery Proceedings Article
In: Workshop on Privacy-Preserving Cyberspace Safety and Security (CSS), 2014.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: DNS-SD, Multicast, Privacy, Service Discovery, Zeroconf | Links:
@inproceedings{Kaiser2014Efficient,
title = {Efficient Privacy Preserving Multicast DNS Service Discovery},
author = {Daniel Kaiser and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Kaiser2014Efficient.pdf},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-08-23},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Workshop on Privacy-Preserving Cyberspace Safety and Security (CSS)},
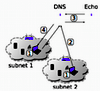
abstract = {In today’s local networks a significant amount of traffic is caused by Multicast DNS Service Discovery (mDNS-SD), a prevalent technique used for configurationless service distribution and discovery. It allows users to offer and use services like device synchronization, file sharing, and chat, when joining a local network without any manual configuration. While this is very convenient, it requires the public exposure of the offering and requesting identities along with information about the offered and requested services, even when services do not need to be public. Some of the information published by the announcements can be very revealing, including complete lists of family members. Another problem is the huge amount of multicast traffic caused, which is especially relevant for large WiFi networks.
In this paper we present a privacy extension that does not publish private information and reduces the number of packets sent while still not requiring any network configuration except for an initial pairing per pair of users. A key feature of our solution is the ease of upgrading existing systems, a must for widespread deployment and acceptance. We developed an implementation based on the open-source Avahi daemon to show the feasibility of our privacy extension. Our solution grants tunable privacy and reduces multicast traffic without affecting user experience.},
keywords = {DNS-SD, Multicast, Privacy, Service Discovery, Zeroconf},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
In this paper we present a privacy extension that does not publish private information and reduces the number of packets sent while still not requiring any network configuration except for an initial pairing per pair of users. A key feature of our solution is the ease of upgrading existing systems, a must for widespread deployment and acceptance. We developed an implementation based on the open-source Avahi daemon to show the feasibility of our privacy extension. Our solution grants tunable privacy and reduces multicast traffic without affecting user experience.
2003
Marcel Waldvogel; Wei Deng; Ramaprabhu Janakiraman
Efficient Buffer Management for Scalable Media-on-Demand Proceedings Article
In: SPIE Multimedia Computing and Networking (MMCN 2003), Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2003.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Video-on-Demand | Links:
@inproceedings{Waldvogel2003Efficient,
title = {Efficient Buffer Management for Scalable Media-on-Demand},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Wei Deng and Ramaprabhu Janakiraman},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2003/waldvogel03efficient.pdf},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-15},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {SPIE Multimedia Computing and Networking (MMCN 2003)},
address = {Santa Clara, CA, USA},
abstract = {<p>Widespread availability of high-speed networks and fast, cheap computation have rendered high-quality Media-on-Demand (MoD) feasible. Research on scalable MoD has resulted in many efficient schemes that involve segmentation and asynchronous broadcast of media data, requiring clients to buffer and reorder out-of-order segments efficiently for serial playout.</p><p>In such schemes, buffer space requirements run to several hundred megabytes and hence require efficient buffer management techniques involving both primary memory and secondary storage: while disk sizes have increased exponentially, access speeds have not kept pace at all.</p><p>The conversion of out-of-order arrival to in-order playout suggests the use of external memory priority queues, but their content-agnostic nature prevents them from performing well under MoD loads. In this paper, we propose and evaluate a series of simple heuristic schemes which, in simulation studies and in combination with our scalable MoD scheme, achieve significant improvements in storage performance over existing schemes.</p>},
keywords = {Multicast, Video-on-Demand},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
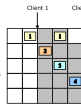
2002
Ramaprabhu Janakiraman; Marcel Waldvogel; Lihao Xu
Fuzzycast: Efficient Video-on-Demand over Multicast Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of INFOCOM, pp. 920-929, New York, NY, USA, 2002.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Video-on-Demand | Links:
@inproceedings{Janakiraman2002Fuzzycast:,
title = {Fuzzycast: Efficient Video-on-Demand over Multicast},
author = {Ramaprabhu Janakiraman and Marcel Waldvogel and Lihao Xu},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2002/janakiraman02fuzzycast.pdf},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-06-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of INFOCOM},
pages = {920-929},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
abstract = { Server bandwidth has been identified as a major bottleneck in large Video-on-Demand (VoD) systems. Using multicast delivery to serve popular content helps increase scalability by making efficient use of server bandwidth. In addition, recent research has focused on proactive schemes in which the server periodically multicasts popular content without explicit requests from clients. Proactive schemes are attractive because they consume bounded server bandwidth irrespective of client arrival rate. In this work, we describe Fuzzycast, a scalable periodic multicast scheme that uses simple techniques to provide video on demand at reasonable client start-up times while consuming optimal server bandwidth. We present a theoretical analysis of its bandwidth and client buffer requirements and prove its optimality. We study the effect of variable bitrate (VBR) media on Fuzzycast performance and propose a simple extension to transmit VBR media over constant rate channels. Finally, we solve the problem of partitioning a transmission over multiple multicast groups by considering it as a specific instance of a more widely encountered resource trade-off. },
keywords = {Multicast, Video-on-Demand},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
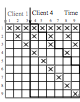
Samphel Norden; Marcel Waldvogel
Imprecise Multicast Routing for Scalable Information Distribution Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of International Zurich Seminar (IZS) 2002, pp. 14-1 – 14-6, Zurich, Switzerland, 2002.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Bloom Filters, Fast Routers, Multicast | Links:
@inproceedings{Norden2002Imprecise,
title = {Imprecise Multicast Routing for Scalable Information Distribution},
author = {Samphel Norden and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2002/norden02imprecise.pdf},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-02-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of International Zurich Seminar (IZS) 2002},
pages = {14-1 -- 14-6},
address = {Zurich, Switzerland},
abstract = {Typically, multicast data distribution uses rendezvous points (PIM, CBT), multicast distribution tree building protocols, and multicast forwarding. Whereas the first two approaches have been extensively studied, scaling multicast forwarding state without increasing forwarding complexity has not been addressed in detail. Having a scalable strategy for aggregation of multicast forwarding state is essential for inter-domain multicast which could have any number of concurrent multicast groups, especially in applications such as event notification and web cache invalidation mechanisms. We first present the essential characteristics of a scalable multicast routing mechanism. We then introduce and analyze, according to these metrics, a scalable aggregation mechanism for multicast-based update and change distribution based on imprecise (too generous) aggregation. Our mechanism is simple to implement, requires no additional information about the groups, and allows important savings in routing table size and routing protocol overhead, at a minimal expense in additional network and end-system traffic.},
keywords = {Bloom Filters, Fast Routers, Multicast},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2001
Dimitris Pendarakis; Sherlia Shi; Dinesh Verma; Marcel Waldvogel
ALMI: An Application Level Multicast Infrastructure Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of the 3rd USENIX Symposium on Internet Technologies and Systems (USITS ’01), pp. 49-60, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@inproceedings{Pendarakis2001ALMI,
title = {ALMI: An Application Level Multicast Infrastructure},
author = {Dimitris Pendarakis and Sherlia Shi and Dinesh Verma and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/pendarakis01almi.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-03-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 3rd USENIX Symposium on Internet Technologies and Systems (USITS '01)},
pages = {49-60},
address = {San Francisco, CA, USA},
abstract = {The IP multicast model allows scalable and efficient multi-party communication, particularly for groups of large size. However, deployment of IP multicast requires substantial infrastructure modifications and is hampered by a host of unresolved open problems. To circumvent this situation, we have designed and implemented ALMI, an application level group communication middleware, which allows accelerated application deployment and simplified network configuration, without the need of network infrastructure support. ALMI is tailored toward support of multicast groups of relatively small size (several 10s of members) with many to many semantics. Session participants are connected via a virtual multicast tree, which consists of unicast connections between end hosts and is formed as a minimum spanning tree (MST) using application-specific performance metric. Using simulation, we show that the performance penalties, introduced by this shift of multicast to end systems, is a relatively small increase in traffic load and that ALMI multicast trees approach the efficiency of IP multicast trees. We have also implemented ALMI as a Java based middleware package and performed experiments over the Internet. Experimental results show that ALMI is able to cope with network dynamics and keep the multicast tree efficient. },
keywords = {Multicast, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
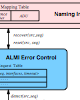
Marcel Waldvogel; Radhesh Mohandas; Sherlia Shi
EKA: Efficient Keyserver using ALMI Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE WET ICE Workshop on Enterprise Security, pp. 237-246, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Security | Links:
@inproceedings{Waldvogel2001EKA,
title = {EKA: Efficient Keyserver using ALMI},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Radhesh Mohandas and Sherlia Shi},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/waldvogel01eka.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE WET ICE Workshop on Enterprise Security},
pages = {237-246},
address = {Cambridge, MA, USA},
abstract = { The keyserver network serves as a repository of OpenPGP keys, providing replication throughout the Internet. It currently uses an inefficient and insufficient protocol to keep its nodes synchronized: highly redundant network traffic and excessive overhead due to several thousand e-mail messages per day. Under these conditions, even short network outages cause massive mail server overloads and losses, resulting in continuously diverging databases. In this paper, we present a new protocol to achieve complete synchronization efficiently and automatically, drastically reducing the need for manual intervention. Our protocol transmits only the updates and uses multicast to optimize the amount of data sent. Since support for native multicast is not widely available in the underlying network and current Internet multicast does not scale well, we base our keyserver on ALMI. ALMI is a middleware for reliable applicationlevel multicast, providing scalable join/leave notification of neighbors, significantly reducing the complexity of the application. As a part of this work, we have also implemented a keyserver software which uses our protocol and an efficient RDBMS back-end to hold the keys. },
keywords = {Multicast, Security},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Marcel Waldvogel; Ramaprabhu Janakiraman; Wei Deng
Fuzzycast: Media Broadcasting for Multiple Asynchronous Receivers Technical Report
Washington University in St. Louis, Department of Computer Science 2001.
BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Video-on-Demand
@techreport{Waldvogel2001Fuzzycast:-techreport,
title = {Fuzzycast: Media Broadcasting for Multiple Asynchronous Receivers},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Ramaprabhu Janakiraman and Wei Deng},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
institution = {Washington University in St. Louis, Department of Computer Science},
keywords = {Multicast, Video-on-Demand},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
Marcel Waldvogel; Wei Deng; Ramaprabhu Janakiraman
Fuzzycast: Media Broadcasting for Multiple Asynchronous Receivers Technical Report
Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri, USA no. WUCS-01-02, 2001.
BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Video-on-Demand
@techreport{Waldvogel2001Media-techreport,
title = {Fuzzycast: Media Broadcasting for Multiple Asynchronous Receivers},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Wei Deng and Ramaprabhu Janakiraman},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {WUCS-01-02},
institution = {Washington University in St. Louis, Missouri, USA},
keywords = {Multicast, Video-on-Demand},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}

Marcel Waldvogel; Ramaprabhu Janakiraman
Efficient Media-on-demand over Multiple Multicast Groups Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of Globecom 2001, San Antonio, Texas, USA, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Video-on-Demand | Links:
@inproceedings{Waldvogel2001Efficient,
title = {Efficient Media-on-demand over Multiple Multicast Groups},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Ramaprabhu Janakiraman},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2004/norden04routing1.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of Globecom 2001},
address = {San Antonio, Texas, USA},
abstract = { Using multicast for serving popular movies on demand reduces load on the server and the network by eliminating redundant packet transmission. To permit clients to arrive at times of their choosing, periodic rebroadcast is necessary. In addition, splitting the transmission over multiple multicast groups reduces the cost of rebroadcasting by allowing clients to unsubscribe from groups in which they are no longer interested.</p><p>The focus of this paper is to develop techniques for efficient Media-on-Demand delivery to asynchronous clients over multiple multicast groups. We start by describing an existing periodic multicast technique that is near-optimal in terms of server bandwidth. Given a small number of groups $alpha$, we then show how to distribute content over these groups in a way that minimizes network impact. We present a theoretical analysis of the performance gains and compare these predictions with simulations over real and generated network topologies. We find that using even a small number of multicast groups provides significant reduction in overall network bandwidth.},
keywords = {Multicast, Video-on-Demand},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Sherlia Shi; Jon Turner; Marcel Waldvogel
Dimensioning Server Access Bandwidth and Multicast Routing in Overlay Networks Proceedings Article
In: Prceedings of NOSSDAV 2001, pp. 83-92, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Traffic Engineering | Links:
@inproceedings{Shi2001Dimensioning,
title = {Dimensioning Server Access Bandwidth and Multicast Routing in Overlay Networks},
author = {Sherlia Shi and Jon Turner and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/shi01dimensioning.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Prceedings of NOSSDAV 2001},
pages = {83-92},
abstract = { Application-level multicast is a new mechanism for enabling multicast in the Internet. Driven by the fast growth of network audio/video streams, application-level multicast has become increasingly important for its efficiency of data delivery and its ability of providing value-added services to satisfy application specific requirements. From a network design perspective, application-level multicast differs drastically from traditional IP multicast in its network cost model and routing strategies. We present these differences and formulate them as a network design problem consisting of two parts: one is bandwidth assignment in the overlay network, the other is load-balancing multicast routing with delay constraints. We use analytical methods and simulations to show that our design solution is a valid and cost-effective approach. Simulation results show that we are able to achieve network utilization within 10% of the best possible utilization while keeping the session rejection rate low.},
keywords = {Multicast, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2000
Sherlia Shi; Marcel Waldvogel
A Rate-based End-to-end Multicast Congestion Control Protocol Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of ISCC 2000, pp. 678-686, Antibes, France, 2000.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Quality of Service | Links:
@inproceedings{Shi2000Rate-based,
title = {A Rate-based End-to-end Multicast Congestion Control Protocol},
author = {Sherlia Shi and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2000/shi00ratebased.pdf},
year = {2000},
date = {2000-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of ISCC 2000},
pages = {678-686},
address = {Antibes, France},
abstract = {Current reliable multicast protocols do not have scalable congestion control mechanisms and this deficiency leads to concerns that multicast deployment may endanger stability of the network. In this paper, we present a sender-based approach for multicast congestion control targeted towards reliable bulk data transfer. We assume that there are a few bottleneck links in a large scale multicast group at any time period and these bottlenecks persist long enough to be identified and adapted to. Our work focus on dynamically identifying the worst congested path in the multicast tree and obtaining TCP-friendly throughput on this selected path. We devise novel selection (amongst receivers) and aggregation (over time) methods to achieve our goal. The response time of our protocol is then compatible to TCP once the worst path is identified. Only when switching between worst paths, the protocol response time is relaxed to multiple RTTs (less than 10) for the reasons of scalability and stability. We use the network simulator (NS2) to validate and evaluate our congestion control algorithm with both drop-tail and RED gateways. },
keywords = {Multicast, Quality of Service},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Sherlia Shi; Marcel Waldvogel
A Rate-based End-to-end Multicast Congestion Control Protocol Technical Report
Department of Computer Science, Washington University in St. Louis no. WUCS-00-03, 2000.
BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Quality of Service | Links:
@techreport{Shi2000Rate-based-techreport,
title = {A Rate-based End-to-end Multicast Congestion Control Protocol},
author = {Sherlia Shi and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2000/shi00ratebased-techreport.pdf},
year = {2000},
date = {2000-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {WUCS-00-03},
institution = {Department of Computer Science, Washington University in St. Louis},
keywords = {Multicast, Quality of Service},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}

1999
Marcel Waldvogel; Germano Caronni; Dan Sun; Nathalie Weiler; Bernhard Plattner
The VersaKey Framework: Versatile Group Key Management Journal Article
In: IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, vol. 17, no. 9, pp. 1614-1631, 1999.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Security | Links:
@article{Waldvogel1999VersaKey,
title = {The VersaKey Framework: Versatile Group Key Management},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Germano Caronni and Dan Sun and Nathalie Weiler and Bernhard Plattner},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/1999/waldvogel99versakey.pdf},
year = {1999},
date = {1999-09-16},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications},
volume = {17},
number = {9},
pages = {1614-1631},
abstract = { Middleware supporting secure applications in a distributed environment faces several challenges. Scalable security in the context of multicasting or broadcasting is especially hard when privacy and authenticity is to be assured to highly dynamic groups where the application allows participants to join and leave at any time. Unicast security is well-known and has widely advanced into production state. But proposals for multicast security solutions that have been published so far are complex, often require trust in network components or are inefficient. In this paper, we propose a framework of new approaches for achieving scalable security in IP multicasting. Our solutions assure that that newly joining members are not able to understand past group traffic, and that leaving members may not follow future communication. For versatility, our framework supports a range of closely related schemes for key management, ranging from tightly centralized to fully distributed and even allows switching between these schemes on-the-fly with low overhead. Operations have low complexity (O(log \textit{N}) for joins and leaves), thus granting scalability even for very large groups. We also present a novel concurrency-enabling scheme, which was devised for fully distributed key management. In this paper we discuss the requirements for secure multicasting, present our flexible system, and evaluate its properties, based on the existing prototype implementation.},
keywords = {Multicast, Security},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
1998
Germano Caronni; Marcel Waldvogel; Dan Sun; Bernhard Plattner
Efficient Security for Large and Dynamic Multicast Groups Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Workshop on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises (WET ICE ’98), Palo Alto, CA, USA, 1998.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Security | Links:
@inproceedings{Caronni1998Efficient,
title = {Efficient Security for Large and Dynamic Multicast Groups},
author = {Germano Caronni and Marcel Waldvogel and Dan Sun and Bernhard Plattner},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/1998/caronni98efficient.pdf},
year = {1998},
date = {1998-06-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE 7th International Workshop on Enabling Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enterprises (WET ICE '98)},
address = {Palo Alto, CA, USA},
abstract = { Proposals for multicast security that have been published so far are complex, often require trust in network components or are inefficient. In this paper we propose a series of novel approaches for achieving scalable security in IP multicast, providing privacy and authentication on a group-wide basis. They can be employed to efficiently secure multi-party applications where members of highly dynamic groups of arbitrary size may participate. Supporting dynamic groups implies that newly joining members must not be able to understand past group communications, and that leaving members may not follow future communications. Key changes are required for all group members when a leave or join occurs, which poses a problem if groups are large. The algorithms presented here require no trust in third parties, support either centralized or fully distributed management of keying material, and have low complexity (O(log N) or less). This grants scalability even for large groups. },
keywords = {Multicast, Security},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Germano Caronni; Marcel Waldvogel; Dan Sun; Bernhard Plattner
Efficient Security for Large and Dynamic Multicast Groups Technical Report
TIK, ETH Zürich no. TIK-41, 1998.
BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Security
@techreport{Caronni1998Efficient-techreport,
title = {Efficient Security for Large and Dynamic Multicast Groups},
author = {Germano Caronni and Marcel Waldvogel and Dan Sun and Bernhard Plattner},
year = {1998},
date = {1998-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {TIK-41},
institution = {TIK, ETH Zürich},
keywords = {Multicast, Security},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}

Germano Caronni; Marcel Waldvogel; Dan Sun; Nathalie Weiler; Bernhard Plattner
VersaKey: Versatile Key Management for Large and Dynamic Multicast Groups Technical Report
TIK, ETH Zürich no. TIK-57, 1998.
BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Security
@techreport{Caronni1998VersaKey-techreport,
title = {VersaKey: Versatile Key Management for Large and Dynamic Multicast Groups},
author = {Germano Caronni and Marcel Waldvogel and Dan Sun and Nathalie Weiler and Bernhard Plattner},
year = {1998},
date = {1998-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {TIK-57},
institution = {TIK, ETH Zürich},
keywords = {Multicast, Security},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}


