General audience texts
Besides the scholarly publications listed below, I have written many texts in English and German. My more notable German texts appeared by DNIP.ch. I also maintain document collections intended for a broad audience:
Scholarly publications
Up-to-date citation counts (provided by Google Scholar). List of patents granted.
2015
Thomas Zink; Marcel Waldvogel
Efficient hash tables for network applications Journal Article
In: SpringerPlus, vol. 4, no. 222, pp. 1-19, 2015.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Hash Tables | Links:
@article{Zink2015EHT,
title = {Efficient hash tables for network applications},
author = {Thomas Zink and Marcel Waldvogel},
editor = {Springer},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/zink2015eht.pdf},
doi = {10.1186/s40064-015-0958-y},
year = {2015},
date = {2015-05-15},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {SpringerPlus},
volume = {4},
number = {222},
pages = {1-19},
abstract = {Hashing has yet to be widely accepted as a component of hard real-time systems and hardware implementations, due to still existing prejudices concerning the unpredictability of space and time requirements resulting from collisions. While in theory perfect hashing can provide optimal mapping, in practice, finding a perfect hash function is too expensive, especially in the context of high-speed applications.
The introduction of hashing with multiple choices, d-left hashing and probabilistic table summaries, has caused a shift towards deterministic DRAM access. However, high amounts of rare and expensive high-speed SRAM need to be traded off for predictability, which is infeasible for many applications.
In this paper we show that previous suggestions suffer from the false precondition of full generality. Our approach exploits four individual degrees of freedom available in many practical applications, especially hardware and high-speed lookups. This reduces the requirement of on-chip memory up to an order of magnitude and guarantees constant lookup and update time at the cost of only minute amounts of additional hardware. Our design makes efficient hash table implementations cheaper, more predictable, and more practical.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Hash Tables},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
The introduction of hashing with multiple choices, d-left hashing and probabilistic table summaries, has caused a shift towards deterministic DRAM access. However, high amounts of rare and expensive high-speed SRAM need to be traded off for predictability, which is infeasible for many applications.
In this paper we show that previous suggestions suffer from the false precondition of full generality. Our approach exploits four individual degrees of freedom available in many practical applications, especially hardware and high-speed lookups. This reduces the requirement of on-chip memory up to an order of magnitude and guarantees constant lookup and update time at the cost of only minute amounts of additional hardware. Our design makes efficient hash table implementations cheaper, more predictable, and more practical.
2009
Thomas Zink; Marcel Waldvogel
Packet Forwarding using Efficient Hash Tables Technical Report
University of Konstanz Konstanz, Germany, no. KN-2009-DISY-01, 2009.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Hash Tables | Links:
@techreport{Zink2009Packet,
title = {Packet Forwarding using Efficient Hash Tables},
author = {Thomas Zink and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/zink2009packet.pdf},
year = {2009},
date = {2009-04-03},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {KN-2009-DISY-01},
address = {Konstanz, Germany},
institution = {University of Konstanz},
abstract = {This report discusses our proposed improvements to Fast Hash Tables (FHT) which we name ’Efficient Hash Table’ (EHT) where ’efficient’ relates to both memory efficiency and lookup performance. The mechanism we use to design the EHT lead to improvements in terms of SRAM memory requirements by the factor of ten over the FHT. Our results back the theoretical analysis and allow accurate predictions. A cost function is provided that allows the adjustment of EHT parameter to different user requirements.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Hash Tables},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
2003
Marcel Waldvogel; Roberto Rinaldi
Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network Journal Article
In: ACM Computer Communications Review, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 101-106, 2003, (Proceedings of ACM HotNets-I (October 2002)).
BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer, Traffic Engineering
@article{Waldvogel2003Efficienta,
title = {Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Roberto Rinaldi},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {ACM Computer Communications Review},
volume = {33},
number = {1},
pages = {101-106},
note = {Proceedings of ACM HotNets-I (October 2002)},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
James Allen; Brian Bass; Claude Basso; Rick Boivie; Jean Calvignac; Gordon Davis; Laurent Freléchoux; Marco Heddes; Andreas Herkersdorf; Andreas Kind; Joe Logan; Mohammad Peyravian; Mark Rinaldi; Ravi Sabhikhi; Michael Siegel; Marcel Waldvogel
IBM PowerNP Network Processor: Hardware Software and Applications Journal Article
In: IBM Journal of Research and Development, vol. 47, no. 2/3, pp. 177-194, 2003.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Network Processors, Quality of Service | Links:
@article{Allen2003PowerNP,
title = {IBM PowerNP Network Processor: Hardware Software and Applications},
author = {James Allen and Brian Bass and Claude Basso and Rick Boivie and Jean Calvignac and Gordon Davis and Laurent Freléchoux and Marco Heddes and Andreas Herkersdorf and Andreas Kind and Joe Logan and Mohammad Peyravian and Mark Rinaldi and Ravi Sabhikhi and Michael Siegel and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2003/allen03powernp.pdf},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {IBM Journal of Research and Development},
volume = {47},
number = {2/3},
pages = {177-194},
abstract = {Deep packet processing is migrating to the edges of service provider networks to simplify and speed up core functions. On the other hand, the cores of such networks are migrating to the switching of high-speed traffic aggregates, e.g., using switching with dense wavelength division multiplexing (DWDM). As a result, more services will need to be performed at the edges, both on behalf of the core and end users. Associated network equipment will therefore require high flexibility to support evolving high-level services as well as extraordinary performance to deal with the high packet rates. Whereas in the past network equipment were based either on general-purpose processors (GPPs) or application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs), favoring flexibility over speed or vice versa, the network processor approach achieves both flexibility and performance. The key advantage of network processors is that hardware-level performance is complemented by flexible software architecture. In this paper, we describe the IBM PowerNP&tm; NP4GS3 network processor and how it addresses these issues. Its hardware and software design characteristics and its comprehensive base operating software of this network processor make it well suited for a wide range of networking applications.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Network Processors, Quality of Service},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
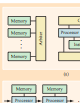
Roman Pletka; Andreas Kind; Marcel Waldvogel; Soenke Mannal
Closed-Loop Congestion Control for Mixed Responsive and Non-Responsive Traffic Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of Globecom 2003, 2003.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Control Engineering, Fast Routers, Traffic Engineering | Links:
@inproceedings{Pletka2003Closed-Loop,
title = {Closed-Loop Congestion Control for Mixed Responsive and Non-Responsive Traffic},
author = {Roman Pletka and Andreas Kind and Marcel Waldvogel and Soenke Mannal},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2003/pletka03closedloop.pdf},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of Globecom 2003},
abstract = {Today's known and widely used active queue management (AQM) schemes do not differentiate between packets from responsive (e.g., TCP sessions) and non-responsive traffic (e.g., UDP). This results in further widening the gap of unfair advantage already inherent to non-responsive traffic, as the responsive sender will significantly reduce its future transmit rate as a result of the congestion signals. As a simple work-around, responsive and non-responsive traffic are often assigned distinct AQM parameters. This approach however requires tuning for each traffic class that potentially depends on the current or expected offered load. In other words, responsiveness and TCP-friendliness cannot be estimated easily—not at last due to short-lived TCP sessions. In this paper we propose a closed-loop congestion control (CLCC) scheme on top of an existing AQM scheme to achieve fair bandwidth distribution among concurrent responsive and non-responsive traffic. The new scheme has the advantage that it does not need to estimate the level of responsiveness of traffic. We analyze our scheme on top of an existing rate-based AQM scheme known to approximate max-min fairness, and by means of simulations show that our extension significantly improves fair bandwidth allocation for responsive and non-responsive traffic. The simulation results have been verified with a prototype implementation on the IBM PowerNP 4GS3 network processor.},
keywords = {Control Engineering, Fast Routers, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2002
Samphel Norden; Marcel Waldvogel
Imprecise Multicast Routing for Scalable Information Distribution Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of International Zurich Seminar (IZS) 2002, pp. 14-1 – 14-6, Zurich, Switzerland, 2002.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Bloom Filters, Fast Routers, Multicast | Links:
@inproceedings{Norden2002Imprecise,
title = {Imprecise Multicast Routing for Scalable Information Distribution},
author = {Samphel Norden and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2002/norden02imprecise.pdf},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-02-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of International Zurich Seminar (IZS) 2002},
pages = {14-1 -- 14-6},
address = {Zurich, Switzerland},
abstract = {Typically, multicast data distribution uses rendezvous points (PIM, CBT), multicast distribution tree building protocols, and multicast forwarding. Whereas the first two approaches have been extensively studied, scaling multicast forwarding state without increasing forwarding complexity has not been addressed in detail. Having a scalable strategy for aggregation of multicast forwarding state is essential for inter-domain multicast which could have any number of concurrent multicast groups, especially in applications such as event notification and web cache invalidation mechanisms. We first present the essential characteristics of a scalable multicast routing mechanism. We then introduce and analyze, according to these metrics, a scalable aggregation mechanism for multicast-based update and change distribution based on imprecise (too generous) aggregation. Our mechanism is simple to implement, requires no additional information about the groups, and allows important savings in routing table size and routing protocol overhead, at a minimal expense in additional network and end-system traffic.},
keywords = {Bloom Filters, Fast Routers, Multicast},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
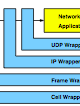
Florian Braun; John Lockwood; Marcel Waldvogel
Protocol Wrappers for Layered Network Packet Processing in Reconfigurable Networks Journal Article
In: IEEE Micro, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 66-74, 2002.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, FPGA | Links:
@article{Braun2002Protocol,
title = {Protocol Wrappers for Layered Network Packet Processing in Reconfigurable Networks},
author = {Florian Braun and John Lockwood and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2002/braun02protocol.pdf},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {IEEE Micro},
volume = {22},
number = {1},
pages = {66-74},
abstract = { A library of layered protocol wrappers has been developed that process Internet packets in reconfigurable hardware. These wrappers can be used with a reprogrammable network platform called the Field Programmable Port Extender (FPX) to rapidly prototype hardware circuits for processing Internet packets. We present a framework to streamline and simplify the development of networking applications that process ATM cells, AAL5 frames, Internet Protocol (IP) packets and UDP datagrams directly in hardware.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, FPGA},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Ken Christensen; Marcel Waldvogel
Issues and Trends in Terabit Switching Journal Article
In: Computer Communications, vol. 25, no. 6, pp. 545–546, 2002.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers | Links:
@article{Christensen2002Issues,
title = {Issues and Trends in Terabit Switching},
author = {Ken Christensen and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/journal/01403664/25/6},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {Computer Communications},
volume = {25},
number = {6},
pages = {545--546},
abstract = {Terabit-per-second switches and routers are already beginning to be commercially available. However, numerous issues still exist in the design of very high-speed switches. Link speeds are now approaching, and exceeding, memory bandwidths, complicating buffer designs. In addition to very high-speed links and large switching capacities, future high-speed switches are expected to be able to support multiple classes of traffic with varying Quality-of-Service (QoS) requirements. This includes traffic classes with guaranteed throughput and bounded delay requirements. Input buffered architectures are being used to deal with memory bandwidth bottlenecks. New challenges arise in switch-matrix and flow-level scheduling. Challenges remain in packet classification. Multistage switching fabrics are being revisited. Network processors are opening new opportunities for supporting high-level capabilities including traffic management. In addition, standardization efforts for switch fabric interfaces are ongoing. Overall, this is an exciting time for switch developers and researchers.},
keywords = {Fast Routers},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Marcel Waldvogel; Roberto Rinaldi
Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network Technical Report
IBM no. RZ-3436, 2002.
BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer
@techreport{Waldvogel2002Efficient-techreport,
title = {Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Roberto Rinaldi},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {RZ-3436},
institution = {IBM},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}

Roberto Rinaldi; Marcel Waldvogel
Routing and Data Location in Overlay Peer-to-Peer Networks Technical Report
IBM no. RZ-3433, 2002.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@techreport{Rinaldi2002Routing-techreport,
title = {Routing and Data Location in Overlay Peer-to-Peer Networks},
author = {Roberto Rinaldi and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2002/waldvogel02topology-techreport.pdf},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {RZ-3433},
institution = {IBM},
abstract = {Peer-to-peer (P2P) networking has become a household word in the past few years, being marketed as a work-around for server scalability problems and “wonder drug” to achieve resilience. Current widely-used P2P networks rely on central directory servers or massive message flooding, clearly not scalable solutions. Distributed Hash Tables (DHT) are expected to eliminate flooding and central servers, but can require many long-haul message deliveries. We introduce Mithos, an overlay network that only uses minimal routing information and is directly suitable for normal and DHT addressing. Unlike other schemes, it also efficiently provides locality-aware connectivity, thereby ensuring that a message reaches its destination with minimal overhead and highly efficient forwarding. The service can in addition be used to support third-party triangulation to point to close replicas of data or services. Its addressing can be mapped directly into a subspace of the IPv6 addresses.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}

2001
Florian Braun; John Lockwood; Marcel Waldvogel
Layered Protocol Wrappers for Internet Packet Processing in Reconfigurable Hardware Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE Hot Interconnects 9, Stanford, CA, USA, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, FPGA | Links:
@inproceedings{Braun2001Layered,
title = {Layered Protocol Wrappers for Internet Packet Processing in Reconfigurable Hardware},
author = {Florian Braun and John Lockwood and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/braun01layered.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-08-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE Hot Interconnects 9},
address = {Stanford, CA, USA},
abstract = { A library of layered protocol wrappers has been developed that process Internet packets in reconfigurable hardware. These wrappers can be used with a reprogrammable network platform called the Field Programmable Port Extender (FPX) to rapidly prototype hardware circuits for processing Internet packets. We present a framework to streamline and simplify the development of networking applications that process ATM cells, AAL5 frames, Internet Protocol (IP) packets and UDP datagrams directly in hardware.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, FPGA},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Marcel Waldvogel; George Varghese; Jon Turner; Bernhard Plattner
Scalable High-Speed Prefix Matching Journal Article
In: Transaction on Computer Systems, vol. 19, no. 4, pp. 440-482, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Hash Tables | Links:
@article{Waldvogel2001Scalable,
title = {Scalable High-Speed Prefix Matching},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and George Varghese and Jon Turner and Bernhard Plattner},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/waldvogel01scalable.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-06-21},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {Transaction on Computer Systems},
volume = {19},
number = {4},
pages = {440-482},
abstract = {Finding the longest matching prefix from a database of keywords is an old problem with a number of applications, ranging from dictionary searches to advanced memory management to computational geometry. But perhaps today's most frequent best matching prefix lookups occur in the Internet, when forwarding packets from router to router. Internet traffic volume and link speeds are rapidly increasing; at the same time, a growing user population is increasing the size of routing tables against which packets must be matched. Both factors make router prefix matching extremely performance critical.In this paper, we introduce a taxonomy for prefix matching technologies, which we use as a basis for describing, categorizing, and comparing existing approaches. We then present in detail a fast scheme using binary search over hash tables, which is especially suited for matching long addresses, such as the 128 bit addresses proposed for use in the next generation Internet Protocol, IPv6. We also present optimizations that exploit the structure of existing databases to further improve access time and reduce storage space.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Hash Tables},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Florian Braun; John Lockwood; Marcel Waldvogel
Reconfigurable Router Modules Using Network Protocol Wrappers Proceedings Article
In: Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL), pp. 254–263, Belfast, Northern Ireland, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, FPGA | Links:
@inproceedings{Braun2001Reconfigurable,
title = {Reconfigurable Router Modules Using Network Protocol Wrappers},
author = {Florian Braun and John Lockwood and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/braun01reconfigurable.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL)},
pages = {254--263},
address = {Belfast, Northern Ireland},
abstract = { A library of layered protocol wrappers has been developed that process Internet packets in reconfigurable hardware. These wrappers can be used with a reprogrammable network platform called the Field Programmable Port Extender (FPX) to rapidly prototype hardware circuits for processing Internet packets. We present a framework to streamline and simplify the development of networking applications that process ATM cells, AAL5 frames, Internet Protocol (IP) packets and UDP datagrams directly in hardware. },
keywords = {Fast Routers, FPGA},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Florian Braun; Marcel Waldvogel; John Lockwood
OBIWAN — An Internet Protocol Router in Reconfigurable Hardware Technical Report
Washington University in St. Louis no. WU-CS-01-11, 2001.
BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, FPGA
@techreport{Braun2001OBIWAN-techreport,
title = {OBIWAN -- An Internet Protocol Router in Reconfigurable Hardware},
author = {Florian Braun and Marcel Waldvogel and John Lockwood},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {WU-CS-01-11},
institution = {Washington University in St. Louis},
keywords = {Fast Routers, FPGA},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
Florian Braun; Marcel Waldvogel
Fast Incremental CRC Updates for IP over ATM networks Technical Report
Washington University in St. Louis no. WUCS-01-08, 2001.
BibTeX | Tags: CRC, Fast Routers
@techreport{Braun2001Fast-techreport,
title = {Fast Incremental CRC Updates for IP over ATM networks},
author = {Florian Braun and Marcel Waldvogel},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {WUCS-01-08},
institution = {Washington University in St. Louis},
keywords = {CRC, Fast Routers},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
Florian Braun; John Lockwood; Marcel Waldvogel
Layered Protocol Wrappers for Internet Packet Processing in Reconfigurable Hardware Technical Report
Washington University in St. Louis no. WUCS-01-10, 2001.
BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, FPGA
@techreport{Braun2001Layered-techreport,
title = {Layered Protocol Wrappers for Internet Packet Processing in Reconfigurable Hardware},
author = {Florian Braun and John Lockwood and Marcel Waldvogel},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {WUCS-01-10},
institution = {Washington University in St. Louis},
keywords = {Fast Routers, FPGA},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}

Florian Braun; Marcel Waldvogel
Fast Incremental CRC Updates for IP over ATM networks Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of 2001 IEEE Workshop on High Performance Switching and Routing (HPSR 2001), Dallas, TX, USA, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: CRC, Fast Routers | Links:
@inproceedings{Braun2001Fast,
title = {Fast Incremental CRC Updates for IP over ATM networks},
author = {Florian Braun and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/braun01fast.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of 2001 IEEE Workshop on High Performance Switching and Routing (HPSR 2001)},
address = {Dallas, TX, USA},
abstract = {In response to the increasing network speeds, many operations in IP routers and similar devices are being made more efficient. With the advances in other areas of packet processing, the verification and regeneration of cyclic redundancy check (CRC) codes of the data link layer is likely to become a bottleneck in the near future. In this paper, we present a mechanism to defer CRC verification without compromising reliability. This opens the possibility of incremental updates of the CRC. We introduce a new high-speed technique and present efficient implementations, speeding up CRC processing by a factor of 15. Although the paper and analysis focuses on IP over ATM, the scheme applies to a much wider set of network protocols.},
keywords = {CRC, Fast Routers},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

2000
Marcel Waldvogel
Multi-Dimensional Prefix Matching Using Line Search Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE Local Computer Networks, pp. 200-207, Tampa, FL, USA, 2000.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Hash Tables, Quality of Service | Links:
@inproceedings{Waldvogel2000Multi-Dimensional,
title = {Multi-Dimensional Prefix Matching Using Line Search},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2000/waldvogel00multidimensional.pdf},
year = {2000},
date = {2000-11-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE Local Computer Networks},
pages = {200-207},
address = {Tampa, FL, USA},
abstract = {With the increasing popularity of firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs) and Quality of Service (QoS) routing, packet classification becomes increasingly important in the Internet. The high-performance solutions known so far strongly rely on certain properties of the filter database to match against, such as a small number of distinct prefixes or the absence of conflicts. In this paper, we present Line Search as a two-dimensional generalization of the one-dimensional binary search on prefix lengths, exploiting the advantage given by the different approach therein. This algorithm also works best on the filter databases that are expected to occur most often, but degrades gracefully when these assumptions no longer hold. We also show how to efficiently extend the algorithm to a complete five-dimensional Internet Protocol (IP) and transport header match.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Hash Tables, Quality of Service},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
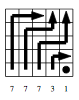
Marcel Waldvogel
Fast Longest Prefix Matching: Algorithms, Analysis, and Applications PhD Thesis
ETH Zürich, 2000.
BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, FPGA
@phdthesis{Waldvogel2000Fasta,
title = {Fast Longest Prefix Matching: Algorithms, Analysis, and Applications},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel},
year = {2000},
date = {2000-05-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {13266},
school = {ETH Zürich},
keywords = {Fast Routers, FPGA},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {phdthesis}
}

Marcel Waldvogel
Fast Longest Prefix Matching: Algorithms, Analysis, and Applications Book
Shaker Verlag, Aachen, Germany, 2000.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Hash Tables | Links:
@book{Waldvogel2000Fast,
title = {Fast Longest Prefix Matching: Algorithms, Analysis, and Applications},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2000/waldvogel00fast.pdf},
year = {2000},
date = {2000-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
publisher = {Shaker Verlag},
address = {Aachen, Germany},
abstract = {Many current problems demand efficient best matching algorithms. Network devices alone show several applications. They need to determine a \emph{longest matching prefix} for packet routing or establishment of virtual circuits. In integrated services packet networks, packets need to be classified by trying to find the \emph{most specific match} from a large number of patterns, each possibly containing wildcards at arbitrary positions. Other areas of applications include such diverse areas as geographical information systems (GIS) and persistent databases.
We describe a class of best matching algorithms based on slicing perpendicular to the patterns and performing a modified binary search over these slices. We also analyze their complexity and performance. We then introduce schemes that allow the algorithm to ``learn'' the structure of the database and adapt itself to it. Furthermore, we show how to efficiently implement our algorithm both using general-purpose hardware and using software running on popular personal computers and workstations.
The research presented herein was originally driven by current demands in the Internet. Since the advent of the World Wide Web, the number of users, hosts, domains, and networks connected to the Internet seems to be exploding. Not surprisingly, network traffic at major exchange points is doubling every few months. The Internet is a packet network, where each data packet is passed from a router to the next in the chain, until it reaches destination. For versatility and efficient utilization of the available transmission bandwidth, each router performs its decision where to forward a packet as independent of the other routers and the other packets for the same destination as possible.
Five key factors are required to keep pace if the Internet is to continue to provide good service:
<ol>
<li>higher link speeds,</li>
<li>better router data throughput,</li>
<li>faster packet forwarding rates,</li>
<li>quick adaptation to topology and load changes, and</li>
<li>the support for Quality-of-Service (QoS).</li>
</ol>
Solutions for the first two are readily available: fiber-optic cables using wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) and switching backplane interconnects. We present longest matching prefix techniques which help solving the other three factors. They allow for a high rate of forwarding decisions, quick updates, and can be extended to classify packets based on multiple fields.
The best known longest matching prefix solutions require memory accesses proportional to the length of the addresses. Our new algorithm uses binary search on hash tables organized by prefix lengths and scales very well as address and routing table sizes increase: independent of the table size, it requires a worst case time of log_{2}(\textit{address bits\textit{) hash lookups. Thus only 5 hash lookups are needed for the current Internet protocol version 4 (IPv4) with 32 address bits and 7 for the upcoming IPv6 with 128 address bits. We also introduce \emph{mutating binary search} and other optimizations that, operating on the largest available databases, reduce the worst case to 4 hashes and allow the majority of addresses to be found with at most 2 hashes. We expect similar improvements to hold for IPv6.
We extend these results to find the best match for a tuple of multiple fields of the packet's header, as required for QoS support. We also show the versatility of the resulting algorithms by using it for such diverse applications as geographical information systems, memory management, garbage collection, persistent object-oriented databases, keeping distributed databases synchronized, and performing web-server access control.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Hash Tables},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {book}
}
We describe a class of best matching algorithms based on slicing perpendicular to the patterns and performing a modified binary search over these slices. We also analyze their complexity and performance. We then introduce schemes that allow the algorithm to “learn” the structure of the database and adapt itself to it. Furthermore, we show how to efficiently implement our algorithm both using general-purpose hardware and using software running on popular personal computers and workstations.
The research presented herein was originally driven by current demands in the Internet. Since the advent of the World Wide Web, the number of users, hosts, domains, and networks connected to the Internet seems to be exploding. Not surprisingly, network traffic at major exchange points is doubling every few months. The Internet is a packet network, where each data packet is passed from a router to the next in the chain, until it reaches destination. For versatility and efficient utilization of the available transmission bandwidth, each router performs its decision where to forward a packet as independent of the other routers and the other packets for the same destination as possible.
Five key factors are required to keep pace if the Internet is to continue to provide good service:
- higher link speeds,
- better router data throughput,
- faster packet forwarding rates,
- quick adaptation to topology and load changes, and
- the support for Quality-of-Service (QoS).
Solutions for the first two are readily available: fiber-optic cables using wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) and switching backplane interconnects. We present longest matching prefix techniques which help solving the other three factors. They allow for a high rate of forwarding decisions, quick updates, and can be extended to classify packets based on multiple fields.
The best known longest matching prefix solutions require memory accesses proportional to the length of the addresses. Our new algorithm uses binary search on hash tables organized by prefix lengths and scales very well as address and routing table sizes increase: independent of the table size, it requires a worst case time of log2(address bits) hash lookups. Thus only 5 hash lookups are needed for the current Internet protocol version 4 (IPv4) with 32 address bits and 7 for the upcoming IPv6 with 128 address bits. We also introduce mutating binary search and other optimizations that, operating on the largest available databases, reduce the worst case to 4 hashes and allow the majority of addresses to be found with at most 2 hashes. We expect similar improvements to hold for IPv6.
We extend these results to find the best match for a tuple of multiple fields of the packet’s header, as required for QoS support. We also show the versatility of the resulting algorithms by using it for such diverse applications as geographical information systems, memory management, garbage collection, persistent object-oriented databases, keeping distributed databases synchronized, and performing web-server access control.

Jonathan Turner; George Varghese; Marcel Waldvogel
Scalable High Speed IP Routing Lookups Miscellaneous
U.S. Patent Number 6,018,524, 2000.
BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Hash Tables
@misc{Turner2000Scalable,
title = {Scalable High Speed IP Routing Lookups},
author = {Jonathan Turner and George Varghese and Marcel Waldvogel},
year = {2000},
date = {2000-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
howpublished = {U.S. Patent Number 6,018,524},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Hash Tables},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {misc}
}

1999
Milind M. Buddhikot; Subhash Suri; Marcel Waldvogel
Space Decomposition Techniques for Fast Layer-4 Switching Proceedings Article
In: Touch, Joseph D.; Sterbenz, James P. G. (Ed.): Protocols for High Speed Networks IV (Proceedings of PfHSN ’99), pp. 25-41, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Salem, MA, USA, 1999, ISBN: 0-7923-8690-6.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Quality of Service, Traffic Engineering | Links:
@inproceedings{Buddhikot1999Space,
title = {Space Decomposition Techniques for Fast Layer-4 Switching},
author = {Milind M. Buddhikot and Subhash Suri and Marcel Waldvogel},
editor = {Joseph D. Touch and James P. G. Sterbenz},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/1999/buddhikot99space.pdf},
isbn = {0-7923-8690-6},
year = {1999},
date = {1999-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Protocols for High Speed Networks IV (Proceedings of PfHSN '99)},
pages = {25-41},
publisher = {Kluwer Academic Publishers},
address = {Salem, MA, USA},
abstract = { Packet classification is the problem of matching each incoming packet at a router against a database of filters, which specify forwarding rules for the packets. The filters are a powerful and uniform way to implement new network services such as firewalls, Network Address Translation (NAT), Virtual Private Networks (VPN), and per-flow or class-based Quality of Service (QOS) guarantees. While several schemes have been proposed recently that can perform packet classification at high speeds, none of them achieves fast worst-case time for adding or deleting filters from the database. In this paper, we present a new scheme, based on space decomposition, whose search time is comparable to the best existing schemes, but which also offers fast worst-case filter update time. The three key ideas in this algorithm are as follows: (1) innovative data-structure based on quadtrees for a hierarchical representation of the recursively decomposed search space, (2) fractional cascading and precomputation to improve packet classification time, and (3) prefix partitioning to improve update time. Depending on the actual requirements of the system this algorithm is deployed in, a single parameter can be used to tradeoff search time for update time. Also, this algorithm is amenable to fast software and hardware implementation.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Quality of Service, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
1998
V. Srinivasan; George Varghese; Subhash Suri; Marcel Waldvogel
Fast and Scalable Layer Four Switching Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM, pp. 191-202, 1998.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Hash Tables, Quality of Service | Links:
@inproceedings{Srinivasan1998Fast,
title = {Fast and Scalable Layer Four Switching},
author = {V. Srinivasan and George Varghese and Subhash Suri and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/1998/srinivasan98fast.pdf},
year = {1998},
date = {1998-09-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM},
pages = {191-202},
abstract = { In Layer Four switching, the route and resources allocated to a packet are determined by the destination address as well as other header fields of the packet such as source address, TCP and UDP port numbers. Layer Four switching unifies firewall processing, RSVP style resource reservation filters, QoS Routing, and normal unicast and multicast forwarding into a single framework. In this framework, the forwarding database of a router consists of a potentially large number of filters on key header fields. A given packet header can match multiple filters, so each filter is given a cost, and the packet is forwarded using the least cost matching filter. In this paper, we describe two new algorithms for solving the least cost matching filter problem at high speeds. Our first algorithm is based on a grid-of-tries construction and works optimally for processing filters consisting of two prefix fields (such as destination-source filters) using linear space. Our second algorithm, cross-producting, provides fast lookup times for arbitrary filters but potentially requires large storage. We describe a combination scheme that combines the advantages of both schemes. The combination scheme can be optimized to handle pure destination prefix filters in 4 memory accesses, destination-source filters in 8 memory accesses worst case, and all other filters in 11 memory accesses in the typical case.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Hash Tables, Quality of Service},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
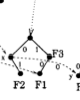
Marcel Waldvogel; George Varghese; Jon Turner; Bernhard Plattner
Scalable Best Matching Prefix Lookups Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of PODC ’98, pp. 311, Puerto Vallarta, México, 1998.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers | Links:
@inproceedings{Waldvogel1998Scalable,
title = {Scalable Best Matching Prefix Lookups},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and George Varghese and Jon Turner and Bernhard Plattner},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/1998/waldvogel98scalable.pdf},
year = {1998},
date = {1998-06-30},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of PODC '98},
pages = {311},
address = {Puerto Vallarta, México},
abstract = {All global routing protocols use hierarchies to allow scaling to a world wide community while keeping the routing database size manageable. Databases of variable length prefixes are a powerful tool for providing this in a flexible manner, but require a Longest Prefix Matching algorithm. In this paper, we report a fundamentally new solution that is both algorithmically interesting and practical.
Our scheme is based on doing binary search on hash tables organized by prefix lengths, and scales very well as address and routing table sizes increase: independent of the table size, it requires a worst case time of log_{2}(\textit{address bits}) hash lookups. With the current Internet Protocol, which uses 32 bit addresses, at most 5 hash lookups are needed; for the upcoming 128 bit addresses of the next generation Internet Protocol (IPv6), 7 lookups suffice. Several refinements, including specializing the Binary Search with every match, considerably reduce the average number of hash search steps to less than 2.},
keywords = {Fast Routers},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Our scheme is based on doing binary search on hash tables organized by prefix lengths, and scales very well as address and routing table sizes increase: independent of the table size, it requires a worst case time of log2(address bits) hash lookups. With the current Internet Protocol, which uses 32 bit addresses, at most 5 hash lookups are needed; for the upcoming 128 bit addresses of the next generation Internet Protocol (IPv6), 7 lookups suffice. Several refinements, including specializing the Binary Search with every match, considerably reduce the average number of hash search steps to less than 2.

1997
Marcel Waldvogel; George Varghese; Jon Turner; Bernhard Plattner
Scalable High Speed IP Routing Table Lookups Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM, pp. 25-36, 1997.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Hash Tables | Links:
@inproceedings{Waldvogel1997Scalable,
title = {Scalable High Speed IP Routing Table Lookups},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and George Varghese and Jon Turner and Bernhard Plattner},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/1997/waldvogel97scalable.pdf},
year = {1997},
date = {1997-08-28},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM},
pages = {25-36},
abstract = {Internet address lookup is a challenging problem because of increasing routing table sizes, increased traffic, higher speed links, and the migration to 128 bit IPv6 addresses. IP routing lookup requires computing the best matching prefix, for which standard solutions like hashing were believed to be inapplicable. The best existing solution we know of, BSD radix tries, scales badly as IP moves to 128 bit addresses. Our paper describes a new algorithm for best matching prefix using binary search on hash tables organized by prefix lengths. Our scheme scales very well as address and routing table sizes increase: independent of the table size, it requires a worst case time of log_{2}(\textit{address bits}) hash lookups. Thus only 5 hash lookups are needed for IPv4 and 7 for IPv6. We also introduce Mutating Binary Search and other optimizations that, for a typical IPv4 backbone router with over 33,000 entries, considerably reduce the average number of hashes to less than 2, of which one hash can be simplified to an indexed array access. We expect similar average case behavior for IPv6.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Hash Tables},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Daniel S. Decasper; Marcel Waldvogel; Zubin Dittia; Adiseshu Hari; Guru Parulkar; Bernhard Plattner
Crossbow — A Toolkit for Integrated Services over Cell Switched IPv6 Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of the IEEE ATM ’97 workshop, Lisboa, Portugal, 1997.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Quality of Service | Links:
@inproceedings{Decasper1997Crossbow,
title = {Crossbow --- A Toolkit for Integrated Services over Cell Switched IPv6},
author = {Daniel S. Decasper and Marcel Waldvogel and Zubin Dittia and Adiseshu Hari and Guru Parulkar and Bernhard Plattner},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/1997/decasper97crossbow.pdf},
year = {1997},
date = {1997-05-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the IEEE ATM '97 workshop},
address = {Lisboa, Portugal},
abstract = {The project Crossbow provides a framework to investigate services and mechanisms including resource management and packet scheduling for multimedia/multicast applications. In particular the Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6, IP next generation, IPng) protocol suite on top of ATM is considered to demonstrate possible synergy between ATM and IPv6. The presented architecture includes IPv6 and RSVP, running on BSD Unix using the 1.2 Gbps APIC (ATM Port Interconnect Controller) chip, as well as support for Ethernet networks.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Quality of Service},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}