General audience texts
Besides the scholarly publications listed below, I have written many texts in English and German. My more notable German texts appeared by DNIP.ch. I also maintain document collections intended for a broad audience:
Scholarly publications
Up-to-date citation counts (provided by Google Scholar). List of patents granted.
2014
Daniel Kaiser; Matthias Fratz; Marcel Waldvogel; Valentin Dietrich; Holger Strittmatter
Stateless DNS Technical Report
University of Konstanz Technical Report, no. KN-2014-DISY-004, 2014.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: DNS-SD, Multicast, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Zeroconf | Links:
@techreport{Kaiser2014Stateless,
title = {Stateless DNS},
author = {Daniel Kaiser and Matthias Fratz and Marcel Waldvogel and Valentin Dietrich and Holger Strittmatter},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/kaiser14stateless.pdf},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-12-31},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {KN-2014-DISY-004},
institution = {University of Konstanz},
abstract = {Several network applications, like service discovery, file discovery in P2P networks, distributed hash tables, and distributed caches, use or would benefit from distributed key value stores. The Domain Name System (DNS) is a key value store which has a huge infrastructure and is accessible from almost everywhere.
Nevertheless storing information in this database makes it necessary to be authoritative for a domain or to be “registered” with a domain, e.g. via DynDNS, to be allowed to store and update resource records using
nsupdate. Applications like the ones listed above would greatly benefit from a configurationless approach, giving users a much more convenient experience.
In this report we describe a technique we call Stateless DNS, which allows to store data in the cache of the local DNS server. It works without any infrastructure updates; it just needs our very simple, configurationless echo DNS server that can parse special queries containing information desired to be stored, process this information, and generate DNS answers in a way that the DNS cache that was asked the special query will store the desired information. Because all this happens in the authority zone of our echo DNS server, we do not cause cache poisoning. Our tests show that Stateless DNS works with a huge number of public DNS servers.},
type = {Technical Report},
keywords = {DNS-SD, Multicast, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Zeroconf},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
Nevertheless storing information in this database makes it necessary to be authoritative for a domain or to be “registered” with a domain, e.g. via DynDNS, to be allowed to store and update resource records using
nsupdate. Applications like the ones listed above would greatly benefit from a configurationless approach, giving users a much more convenient experience.
In this report we describe a technique we call Stateless DNS, which allows to store data in the cache of the local DNS server. It works without any infrastructure updates; it just needs our very simple, configurationless echo DNS server that can parse special queries containing information desired to be stored, process this information, and generate DNS answers in a way that the DNS cache that was asked the special query will store the desired information. Because all this happens in the authority zone of our echo DNS server, we do not cause cache poisoning. Our tests show that Stateless DNS works with a huge number of public DNS servers.
Daniel Kaiser; Marcel Waldvogel
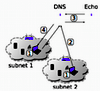
Adding Privacy to Multicast DNS Service Discovery Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE TrustCom 2014 (IEEE EFINS 2014 workshop), 2014.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: DNS-SD, Multicast, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Service Discovery, Social Networks, Trust, Zeroconf | Links:
@inproceedings{Kaiser2014Adding,
title = {Adding Privacy to Multicast DNS Service Discovery},
author = {Daniel Kaiser and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2014/08/Kaiser2014Adding.pdf},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-09-24},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE TrustCom 2014 (IEEE EFINS 2014 workshop)},
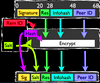
abstract = {Multicast DNS Service Discovery (mDNS-SD), made fashionable through Apple’s \emph{Bonjour}, is a prevalent technique allowing service distribution and discovery in local networks without configuration (Zeroconf). Possible application areas are device synchronization, instant messaging, VoIP, file and screen sharing. It is very convenient for users, because they can connect to and offer services when they enter a network without any manual configuration. However, it requires the public exposure of the offering and requesting identities along with information about the offered and requested services, even when services do not need to be public. Some of the information published by the announcements can be very revealing, including complete lists of family members. In this paper we discuss the privacy problems arising when using mDNS-SD and present our privacy extension, which allows hiding all information published while still not requiring any network configuration except for an initial pairing. A key feature of our solution is the ease of upgrading existing systems, a must for widespread deployment and acceptance. To show the feasibility of our mDNS-SD privacy extension, we developed an implementation based on the open-source \emph{Avahi} daemon.},
keywords = {DNS-SD, Multicast, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Service Discovery, Social Networks, Trust, Zeroconf},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Marcel Waldvogel; Jürgen Kollek
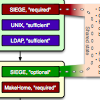
SIEGE: Service-Independent Enterprise-GradE protection against password scans Technical Report
University of Konstanz no. KN-2014-DiSy-001, 2014.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Denial of Service, Intrusion Detection, Peer-to-Peer, Security, Trust | Links:
@techreport{waldvogel4siege,
title = {SIEGE: Service-Independent Enterprise-GradE protection against password scans},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Jürgen Kollek},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2014/01/waldvogel14siege.pdf},
year = {2014},
date = {2014-01-17},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {KN-2014-DiSy-001},
institution = {University of Konstanz},
abstract = {Security is one of the main challenges today, complicated significantly by the heterogeneous and open academic networks with thousands of different applications. Botnet-based brute-force password scans are common security threat against the open academic networks. Common defenses are hard to maintain, error-prone and do not reliably discriminate between user error and coordinated attack. In this paper, we present a novel approach, which allows to secure many network services at once. By combining in-app tracking, local and global crowdsourcing, geographic information, and probabilistic user-bot distinction through differential password analysis, our PAM-based detection module can provide higher accuracy and faster blocking of bot- nets. In the future, we aim to make the mechanism even more generic and thus provide a distributed defense against one of the strongest threats against our infrastructure.},
keywords = {Denial of Service, Intrusion Detection, Peer-to-Peer, Security, Trust},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
2012
Thomas Zink; Marcel Waldvogel
BitTorrent traffic obfuscation: A chase towards semantic traffic identification Proceedings Article
In: 12th IEEE International Conference on Peer-to-Peer Computing, P2P 2012, pp. 126-137, 2012.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Denial of Service, Peer-to-Peer, Security, Traffic Engineering | Links:
@inproceedings{Zink2012BitTorrent,
title = {BitTorrent traffic obfuscation: A chase towards semantic traffic identification},
author = {Thomas Zink and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2012/zink12bittorrent.pdf},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-09-03},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {12th IEEE International Conference on Peer-to-Peer Computing, P2P 2012},
pages = {126-137},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/p2p/2012},
abstract = {With the beginning of the 21st century emerging peer-to-peer networks ushered in a new era of large scale media exchange. Faced with ever increasing volumes of traffic, legal threats by copyright holders, and QoS demands of customers, network service providers are urged to apply traffic classification and shaping techniques. These systems usually are highly integrated to satisfy the harsh restrictions present in network infrastructure. They require constant maintenance and updates. Additionally, they have legal issues and violate both the net neutrality and end-to-end principles. On the other hand, clients see their freedom and privacy attacked. As a result, users, application programmers, and even commercial service providers laboriously strive to hide their interests and circumvent classification techniques. In this user vs. ISP war, the user side has a clear edge. While changing the network infrastructure is by nature very complex, and only slowly reacts to new conditions, updating and distributing software between users is easy and practically instantaneous. In this paper we discuss how state-of-the-art traffic classification systems can be circumvented with little effort. We present a new obfuscation extension to the BitTorrent protocol that allows signature free handshaking. The extension requires no changes to the infrastructure and is fully backwards compatible. With only little change to client software, contemporary classification techniques are rendered ineffective. We argue that future traffic classification must not rely on restricted local syntax information but instead must exploit global communication patterns and protocol semantics in order to be able to keep pace with rapid application and protocol changes.},
keywords = {Denial of Service, Peer-to-Peer, Security, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Thomas Zink; Oliver Haase; Jürgen Wäsch; Marcel Waldvogel
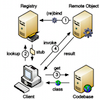
P2P-RMI: Transparent Distribution of Remote Java Objects Journal Article
In: International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC), vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 17-34, 2012.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Java RMI, NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer, Service Discovery | Links:
@article{Zink2012P2P-RMI,
title = {P2P-RMI: Transparent Distribution of Remote Java Objects},
author = {Thomas Zink and Oliver Haase and Jürgen Wäsch and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/zink2012p2p-rmi.pdf},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-09-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC)},
volume = {4},
number = {5},
pages = {17-34},
abstract = {Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) is a built-in and easy-to-use framework for the distribution of remote Java objects. Its simplicity and seamless inter-virtual machine communication has made it a valuable tool for distributed services. It nevertheless exhibits certain constraints that practically limit RMI applications to the classical client/server distribution model, and make highly distributed and highly dynamic systems very difficult to build atop RMI.
We present an approach that makes Java RMI usable for P2P and similar distribution models. The solution basically consists of three ideas: (1) separate the location of the registry from the remote service object, (2) distribute the registry across a DHT infrastructure, and (3) transparently enhance the built-in communication between RMI servers and clients to allow traversal of NAT and firewall boundaries. Our approach is extremely lightweight, transparent, and requires practically zero configuration.},
keywords = {Java RMI, NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer, Service Discovery},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
We present an approach that makes Java RMI usable for P2P and similar distribution models. The solution basically consists of three ideas: (1) separate the location of the registry from the remote service object, (2) distribute the registry across a DHT infrastructure, and (3) transparently enhance the built-in communication between RMI servers and clients to allow traversal of NAT and firewall boundaries. Our approach is extremely lightweight, transparent, and requires practically zero configuration.
Thomas Zink; Marcel Waldvogel
Efficient BitTorrent handshake obfuscation Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of the First Workshop on P2P and Dependability, ACM, 2012, ISBN: 978-1-4503-1148-9.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Security, Traffic Engineering | Links:
@inproceedings{Zink2012Efficient,
title = {Efficient BitTorrent handshake obfuscation},
author = {Thomas Zink and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/zink2012efficient.pdf},
isbn = {978-1-4503-1148-9},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-05-08},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the First Workshop on P2P and Dependability},
publisher = {ACM},
abstract = {During the last decade, large scale media distribution populated peer-to-peer applications. Faced with ever increasing volumes of traffic, legal threats by copyright holders, and QoS demands of customers, network service providers are urged to apply traffic classification and shaping techniques. These highly integrated systems require constant maintenance, introduce legal issues, and violate both the net neutrality and end-to-end principles.
Clients see their freedom and privacy attacked. Users, application programmers, and even commercial service providers laboriously strive to hide their interests and circumvent classification techniques. While changing the network infrastructure is by nature very complex, and it reacts only slowly to new conditions, updating and distributing software between users is easy and practically instantaneous.
We present a new obfuscation extension to the BitTorrent protocol, which allows signature free handshaking. The extension requires no changes to the infrastructure and is fully backwards compatible. With only little change to client software, contemporary classification techniques can be rendered ineffective.},
keywords = {Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Security, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Clients see their freedom and privacy attacked. Users, application programmers, and even commercial service providers laboriously strive to hide their interests and circumvent classification techniques. While changing the network infrastructure is by nature very complex, and it reacts only slowly to new conditions, updating and distributing software between users is easy and practically instantaneous.
We present a new obfuscation extension to the BitTorrent protocol, which allows signature free handshaking. The extension requires no changes to the infrastructure and is fully backwards compatible. With only little change to client software, contemporary classification techniques can be rendered ineffective.
2011
Daniel Maier; Oliver Haase; Jürgen Wäsch; Marcel Waldvogel
A Comparative Analysis of NAT Hole Punching Journal Article
In: HTWG Forum, pp. 40-48, 2011, ISSN: 1619-9812.
BibTeX | Tags: NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@article{Maier2011Comparative,
title = {A Comparative Analysis of NAT Hole Punching},
author = {Daniel Maier and Oliver Haase and Jürgen Wäsch and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2011/maier11comparative.pdf},
issn = {1619-9812},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-11-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {HTWG Forum},
pages = {40-48},
keywords = {NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Daniel Maier; Oliver Haase; Jürgen Wäsch; Marcel Waldvogel
NAT Hole Punching Revisited Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE LCN 2011, The 36th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, 2011.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@inproceedings{Maier2011NAT,
title = {NAT Hole Punching Revisited},
author = {Daniel Maier and Oliver Haase and Jürgen Wäsch and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2011/maier11nat.pdf},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-10-07},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE LCN 2011, The 36th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks},
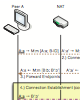
abstract = {Setting up connections to hosts behind Network Address Translation (NAT) equipment has last been the subject of research debates half a decade ago when NAT technology was still immature. This paper fills this gap and provides a solid comparison of two essential TCP hole punching approaches: sequential and parallel TCP hole punching. The comparison features current conditions and thoroughly compares setup delay, implementation complexity, resource usage, and effectuality of the two approaches. The result is a list of recommendations and a portable, effectual, and open-source Java implementation.},
keywords = {NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2010
Thomas Zink; Marcel Waldvogel
Analysis and Efficient Classification of P2P File Sharing Traffic Technical Report
University of Konstanz Konstanz, Germany, no. KN-2010-DISY-02, 2010.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Peer-to-Peer, Security, Traffic Engineering | Links:
@techreport{Zink2010Analysis,
title = {Analysis and Efficient Classification of P2P File Sharing Traffic},
author = {Thomas Zink and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/zink2010analysis.pdf},
year = {2010},
date = {2010-10-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {KN-2010-DISY-02},
address = {Konstanz, Germany},
institution = {University of Konstanz},
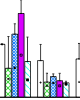
abstract = {Since the advent of P2P networks they have grown to be the biggest source of internet traffic, superseding HTTP and FTP. For service providers P2P traffic results in increased costs for both infrastructure and transportation. Interest is high to reliably identify the type of service to ensure quality of service. In this document we analyze P2P network architectures and give an overview of existing identification mechanisms. In addition we devise a simple identification scheme suitable for implementation in resources restricted environments with limited computational power and memory. The scheme is based on behavior analysis and as such is not prone to traffic obfuscation techniques.},
keywords = {Peer-to-Peer, Security, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
2008
Sebastian Kay Belle; Marcel Waldvogel
Consistent Deniable Lying: Privacy in Mobile Social Networks Proceedings Article
In: Pervasive 2008 Workshop on Security and Privacy Issues in Mobile Phone Use (SPMU 2008), Sydney, Australia, 2008.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Opportunistic Networks, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Security, Social Networks | Links:
@inproceedings{Belle2008Consistent,
title = {Consistent Deniable Lying: Privacy in Mobile Social Networks},
author = {Sebastian Kay Belle and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2008/belle08consistent.pdf},
year = {2008},
date = {2008-05-19},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Pervasive 2008 Workshop on Security and Privacy Issues in Mobile Phone Use (SPMU 2008)},
address = {Sydney, Australia},
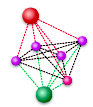
abstract = {Social networking is moving to mobile phones. This not only means continuous access, but also allows to link virtual and physical neighbourhood in novel ways. To make such systems useful, personal data such as lists of friends and interests need to be shared with more and frequently unknown people, posing a risk to your privacy. In this paper, we present our approach to social networking, Consistent Deniable Lying (CDL). Using easy-to-understand mechanisms and tuned to this environment, it enables you to meet new friends with joint interests while limiting exposure of your private data. Not only can it be generalised to include “friends of friends” (transitivity) into interest search, it allows you to plausibly refute any allegations of your claimed interests. Unlike prior work, we focus on the application to similarity finding and include the novel aspects of transitivity and deniability, which are key to success in social networks.},
keywords = {Opportunistic Networks, Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Security, Social Networks},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2007
Daniel Bauer; Paul Hurley; Marcel Waldvogel
Replica Placement and Location using Distributed Hash Tables Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE LCN, pp. 315-324, 2007, ISBN: 0-7695-3000-1.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Peer-to-Peer, Replication | Links:
@inproceedings{Bauer2007Replica,
title = {Replica Placement and Location using Distributed Hash Tables},
author = {Daniel Bauer and Paul Hurley and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2007/bauer07replica.pdf},
isbn = {0-7695-3000-1},
year = {2007},
date = {2007-10-15},
urldate = {2007-10-15},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE LCN},
pages = {315-324},
crossref = {DBLP:conf/lcn/2007},
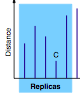
abstract = {Interest in distributed storage is fueled by demand for reliability and resilience combined with decreasing hardware costs. Peer-to-peer storage networks based on distributed hash tables are attractive for their efficient use of resources and resulting performance. The placement and subsequent efficient location of replicas in such systems remain open problems, especially (1) the requirement to update replicated content, (2) working in the absence of global information, and (3) determination of the locations in a dynamic system without introducing single points of failure. We present and evaluate a novel and versatile technique, replica enumeration, which allows for controlled replication and replica access. The possibility of enumerating and addressing individual replicas allows dynamic updates as well as superior performance without burdening the network with state information, yet taking advantage of locality information when available. We simulate, analyze, and prove properties of the system, and discuss some applications.},
keywords = {Peer-to-Peer, Replication},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2004
Daniel Bauer; Paul Hurley; Roman Pletka; Marcel Waldvogel
Bringing Efficient Advanced Queries to Distributed Hash Tables Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE LCN, 2004.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@inproceedings{Bauer2004Bringing,
title = {Bringing Efficient Advanced Queries to Distributed Hash Tables},
author = {Daniel Bauer and Paul Hurley and Roman Pletka and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2004/bauer04bringing.pdf},
year = {2004},
date = {2004-11-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE LCN},
abstract = {Interest in distributed storage is fueled by demand for reliability and resilience combined with ubiquitous availability. Peer-to-peer (P2P) storage networks are known for their decentralized control, self-organization, and adaptation. Advanced searching for documents and resources remains an open problem. The flooding approach favored by some P2P networks is ineffiencient in resource usage, but more scalable and resource-efficient solutions based on Distributed Hash Tables (DHT) lack in query expressiveness and flexibility. In this paper, we address this issue and introduce new efficient, scalable, and completely distributed methods that strive to keep resource consumption by queries and index information as low as possible. We describe how to improve the handling of multiple subqueries combined through boolean set operators. The need for these operators is intensified by applications to go beyond simple exact keyword matches. We discuss, optimize, and analyze appropriate extensions to support range and prefix matching in DHTs.},
keywords = {Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
2003
Germano Caronni; Marcel Waldvogel
Establishing Trust in Distributed Storage Providers Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of Third IEEE International Conference on Peer-to-Peer Computing (P2P 2003), 2003.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Cloud Storage, Peer-to-Peer, Replication, Trust | Links:
@inproceedings{Caronni2003Establishing,
title = {Establishing Trust in Distributed Storage Providers},
author = {Germano Caronni and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2003/caronni03establishing.pdf},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-09-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of Third IEEE International Conference on Peer-to-Peer Computing (P2P 2003)},
abstract = {Corporate IT as well as individuals show increasing interest in reliable outsourcing of storage infrastructure. Decentralized solutions with their resilience against partial outages are among the most attractive approaches. Irrespective of the form of the relationship, be it based on a contract or on the more flexible cooperative model, the problem of verifying whether someone promising to store one's data actually does so remains to be solved, especially in the presence of multiple replicas. In this paper, we introduce a lightweight mechanism that allows the \textit{data originator} or a dedicated \textit{verification agent} to build up trust in the \textit{replica holder} by means of protocols that do not require prior trust or key establishment. We show how naive versions of the protocol do not prevent cheating, and then strengthen it by adding means that make it economically attractive to be honest. This provides a foundation for further work in providing trustworthy distributed storage.},
keywords = {Cloud Storage, Peer-to-Peer, Replication, Trust},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Marcel Waldvogel; Paul Hurley; Daniel Bauer
Dynamic Replica Management in Distributed Hash Tables Technical Report
IBM no. RZ–3502, 2003.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Peer-to-Peer, Replication | Links:
@techreport{Waldvogel2003Dynamic-techreport,
title = {Dynamic Replica Management in Distributed Hash Tables},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Paul Hurley and Daniel Bauer},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2003/waldvogel03dynamic-techreport.pdf},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-07-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {RZ--3502},
institution = {IBM},
abstract = {Interest in distributed storage is fueled by demand for reliability and resilience combined with decreasing hardware costs. Peer-to-peer storage networks based on distributed hash tables are an attractive solution due to their efficient use of resources and resulting performance. The placement and subsequent efficient location of replicas in such systems remain open problems, especially<ol><li>the requirement to update replicated content,</li><li>working in the absence of global information, and</li><li>how to determine the locations in a dynamic system without introducing single points of failure.</li></ol>We present and evaluate a novel and versatile technique, replica enumeration, which allows for controlled replication and replica access. The possibility of enumerating and addressing individual replicas allows dynamic updates as well as superior performance without burdening the network with state information, yet taking advantage of locality information when available. We simulate, analyze, and prove properties of the system, and discuss some applications.},
keywords = {Peer-to-Peer, Replication},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}
- the requirement to update replicated content,
- working in the absence of global information, and
- how to determine the locations in a dynamic system without introducing single points of failure.
Marcel Waldvogel; Roberto Rinaldi
Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network Journal Article
In: ACM Computer Communications Review, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 101-106, 2003, (Proceedings of ACM HotNets-I (October 2002)).
BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer, Traffic Engineering
@article{Waldvogel2003Efficienta,
title = {Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Roberto Rinaldi},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {ACM Computer Communications Review},
volume = {33},
number = {1},
pages = {101-106},
note = {Proceedings of ACM HotNets-I (October 2002)},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
2002
Marcel Waldvogel; Roberto Rinaldi
Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of ACM HotNets-I, 2002.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@inproceedings{Waldvogel2002Efficient,
title = {Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Roberto Rinaldi},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2003/waldvogel03efficient.pdf},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-10-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of ACM HotNets-I},
abstract = {Peer-to-peer (P2P) networking has become a household word in the past few years, being marketed as a work-around for server scalability problems and ``wonder drug'' to achieve resilience. Current widely-used P2P networks rely on central directory servers or massive message flooding, clearly not scalable solutions. Distributed Hash Tables (DHT) are expected to eliminate flooding and central servers, but can require many long-haul message deliveries. We introduce Mithos, an content-addressable overlay network that only uses minimal routing information and is directly suitable as an underlay network for P2P systems, both using traditional and DHT addressing. Unlike other schemes, it also efficiently provides locality-aware connectivity, thereby ensuring that a message reaches its destination with minimal overhead. Mithos provides for highly efficient forwarding, making it suitable for use in high-throughput applications. Paired with its ability to have addresses directly mapped into a subspace of the IPv6 address space, it provides a potential candidate for native deployment. Additionally, Mithos can be used to support third-party triangulation to quickly select a close-by replica of data or services.},
keywords = {Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}

Marcel Waldvogel; Roberto Rinaldi
Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network Technical Report
IBM no. RZ-3436, 2002.
BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer
@techreport{Waldvogel2002Efficient-techreport,
title = {Efficient Topology-Aware Overlay Network},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Roberto Rinaldi},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {RZ-3436},
institution = {IBM},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}

Roberto Rinaldi; Marcel Waldvogel
Routing and Data Location in Overlay Peer-to-Peer Networks Technical Report
IBM no. RZ-3433, 2002.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@techreport{Rinaldi2002Routing-techreport,
title = {Routing and Data Location in Overlay Peer-to-Peer Networks},
author = {Roberto Rinaldi and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2002/waldvogel02topology-techreport.pdf},
year = {2002},
date = {2002-01-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
number = {RZ-3433},
institution = {IBM},
abstract = {Peer-to-peer (P2P) networking has become a household word in the past few years, being marketed as a work-around for server scalability problems and “wonder drug” to achieve resilience. Current widely-used P2P networks rely on central directory servers or massive message flooding, clearly not scalable solutions. Distributed Hash Tables (DHT) are expected to eliminate flooding and central servers, but can require many long-haul message deliveries. We introduce Mithos, an overlay network that only uses minimal routing information and is directly suitable for normal and DHT addressing. Unlike other schemes, it also efficiently provides locality-aware connectivity, thereby ensuring that a message reaches its destination with minimal overhead and highly efficient forwarding. The service can in addition be used to support third-party triangulation to point to close replicas of data or services. Its addressing can be mapped directly into a subspace of the IPv6 addresses.},
keywords = {Fast Routers, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {techreport}
}

2001
Dimitris Pendarakis; Sherlia Shi; Dinesh Verma; Marcel Waldvogel
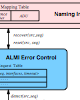
ALMI: An Application Level Multicast Infrastructure Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of the 3rd USENIX Symposium on Internet Technologies and Systems (USITS ’01), pp. 49-60, San Francisco, CA, USA, 2001.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Multicast, Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@inproceedings{Pendarakis2001ALMI,
title = {ALMI: An Application Level Multicast Infrastructure},
author = {Dimitris Pendarakis and Sherlia Shi and Dinesh Verma and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/pendarakis01almi.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-03-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the 3rd USENIX Symposium on Internet Technologies and Systems (USITS '01)},
pages = {49-60},
address = {San Francisco, CA, USA},
abstract = {The IP multicast model allows scalable and efficient multi-party communication, particularly for groups of large size. However, deployment of IP multicast requires substantial infrastructure modifications and is hampered by a host of unresolved open problems. To circumvent this situation, we have designed and implemented ALMI, an application level group communication middleware, which allows accelerated application deployment and simplified network configuration, without the need of network infrastructure support. ALMI is tailored toward support of multicast groups of relatively small size (several 10s of members) with many to many semantics. Session participants are connected via a virtual multicast tree, which consists of unicast connections between end hosts and is formed as a minimum spanning tree (MST) using application-specific performance metric. Using simulation, we show that the performance penalties, introduced by this shift of multicast to end systems, is a relatively small increase in traffic load and that ALMI multicast trees approach the efficiency of IP multicast trees. We have also implemented ALMI as a Java based middleware package and performed experiments over the Internet. Experimental results show that ALMI is able to cope with network dynamics and keep the multicast tree efficient. },
keywords = {Multicast, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}