Abstract
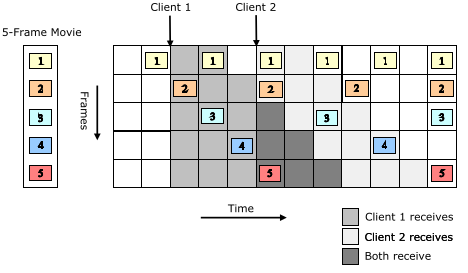
<p>Widespread availability of high-speed networks and fast, cheap computation have rendered high-quality Media-on-Demand (MoD) feasible. Research on scalable MoD has resulted in many efficient schemes that involve segmentation and asynchronous broadcast of media data, requiring clients to buffer and reorder out-of-order segments efficiently for serial playout.</p><p>In such schemes, buffer space requirements run to several hundred megabytes and hence require efficient buffer management techniques involving both primary memory and secondary storage: while disk sizes have increased exponentially, access speeds have not kept pace at all.</p><p>The conversion of out-of-order arrival to in-order playout suggests the use of external memory priority queues, but their content-agnostic nature prevents them from performing well under MoD loads. In this paper, we propose and evaluate a series of simple heuristic schemes which, in simulation studies and in combination with our scalable MoD scheme, achieve significant improvements in storage performance over existing schemes.</p>
BibTeX (Download)
@inproceedings{Waldvogel2003Efficient,
title = {Efficient Buffer Management for Scalable Media-on-Demand},
author = {Marcel Waldvogel and Wei Deng and Ramaprabhu Janakiraman},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2003/waldvogel03efficient.pdf},
year = {2003},
date = {2003-01-15},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {SPIE Multimedia Computing and Networking (MMCN 2003)},
address = {Santa Clara, CA, USA},
abstract = {<p>Widespread availability of high-speed networks and fast, cheap computation have rendered high-quality Media-on-Demand (MoD) feasible. Research on scalable MoD has resulted in many efficient schemes that involve segmentation and asynchronous broadcast of media data, requiring clients to buffer and reorder out-of-order segments efficiently for serial playout.</p><p>In such schemes, buffer space requirements run to several hundred megabytes and hence require efficient buffer management techniques involving both primary memory and secondary storage: while disk sizes have increased exponentially, access speeds have not kept pace at all.</p><p>The conversion of out-of-order arrival to in-order playout suggests the use of external memory priority queues, but their content-agnostic nature prevents them from performing well under MoD loads. In this paper, we propose and evaluate a series of simple heuristic schemes which, in simulation studies and in combination with our scalable MoD scheme, achieve significant improvements in storage performance over existing schemes.</p>},
keywords = {Multicast, Video-on-Demand},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}