Links
Abstract
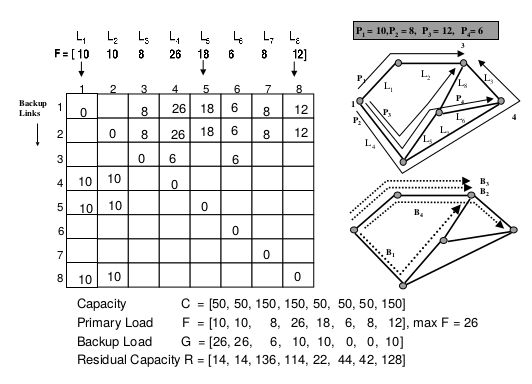
Label switched networks have become increasingly attractive to both network providers and customers. By creating aggregate, bandwidth-reserved flows, these networks are known for their routing flexibility, predictable bandwidth usage, and quality-of-service (QoS) provisioning. This flexibility in routing enables fault-persistent QoS reservations, where connectivity and allotted bandwidth remains available, even if some links or network nodes fail. The automatic switch-over from a now-defunct path to a new, working path is known as restoration. Restoring bandwidth-guaranteed paths requires allocation of resources to be used in presence of faults, so-called backup paths. In this paper, we investigate distributed algorithms for routing with backup restoration. Specifically, we propose a new concept of Backup Load Distribution Matrix, that captures partial network state, greatly reducing the amount of routing information maintained and transmitted while achieving efficient bandwidth usage. We present and simulate two new distributed routing algorithms, which provide significant improvements in rejection rates and provide substantial savings in call setup time compared to existing algorithms.
BibTeX (Download)
@inproceedings{Norden2001Routing,
title = {Routing Bandwidth Guaranteed Paths with Restoration in Label Switched Networks},
author = {Samphel Norden and Milind M. Buddhikot and Marcel Waldvogel and Subhash Suri},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2001/norden01routing.pdf},
year = {2001},
date = {2001-11-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Network Protocols (ICNP 2001)},
pages = {71-79},
address = {Riverside, CA, USA},
abstract = { Label switched networks have become increasingly attractive to both network providers and customers. By creating aggregate, bandwidth-reserved flows, these networks are known for their routing flexibility, predictable bandwidth usage, and quality-of-service (QoS) provisioning. This flexibility in routing enables fault-persistent QoS reservations, where connectivity and allotted bandwidth remains available, even if some links or network nodes fail. The automatic switch-over from a now-defunct path to a new, working path is known as restoration. Restoring bandwidth-guaranteed paths requires allocation of resources to be used in presence of faults, so-called backup paths. In this paper, we investigate distributed algorithms for routing with backup restoration. Specifically, we propose a new concept of Backup Load Distribution Matrix, that captures partial network state, greatly reducing the amount of routing information maintained and transmitted while achieving efficient bandwidth usage. We present and simulate two new distributed routing algorithms, which provide significant improvements in rejection rates and provide substantial savings in call setup time compared to existing algorithms.},
keywords = {Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}