Abstract
During the last decade, large scale media distribution populated peer-to-peer applications. Faced with ever increasing volumes of traffic, legal threats by copyright holders, and QoS demands of customers, network service providers are urged to apply traffic classification and shaping techniques. These highly integrated systems require constant maintenance, introduce legal issues, and violate both the net neutrality and end-to-end principles.
Clients see their freedom and privacy attacked. Users, application programmers, and even commercial service providers laboriously strive to hide their interests and circumvent classification techniques. While changing the network infrastructure is by nature very complex, and it reacts only slowly to new conditions, updating and distributing software between users is easy and practically instantaneous.
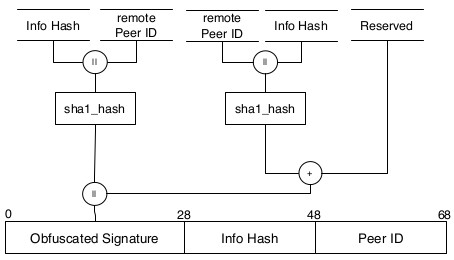
We present a new obfuscation extension to the BitTorrent protocol, which allows signature free handshaking. The extension requires no changes to the infrastructure and is fully backwards compatible. With only little change to client software, contemporary classification techniques can be rendered ineffective.
BibTeX (Download)
@inproceedings{Zink2012Efficient,
title = {Efficient BitTorrent handshake obfuscation},
author = {Thomas Zink and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/zink2012efficient.pdf},
isbn = {978-1-4503-1148-9},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-05-08},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the First Workshop on P2P and Dependability},
publisher = {ACM},
abstract = {During the last decade, large scale media distribution populated peer-to-peer applications. Faced with ever increasing volumes of traffic, legal threats by copyright holders, and QoS demands of customers, network service providers are urged to apply traffic classification and shaping techniques. These highly integrated systems require constant maintenance, introduce legal issues, and violate both the net neutrality and end-to-end principles.
Clients see their freedom and privacy attacked. Users, application programmers, and even commercial service providers laboriously strive to hide their interests and circumvent classification techniques. While changing the network infrastructure is by nature very complex, and it reacts only slowly to new conditions, updating and distributing software between users is easy and practically instantaneous.
We present a new obfuscation extension to the BitTorrent protocol, which allows signature free handshaking. The extension requires no changes to the infrastructure and is fully backwards compatible. With only little change to client software, contemporary classification techniques can be rendered ineffective.},
keywords = {Peer-to-Peer, Privacy, Security, Traffic Engineering},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}