Aktuelle Zitatinformationen meiner Publikationen (bereitgestellt durch Google Scholar). Falls Sie sich nur für die wenigen Publikationen auf Deutsch interessieren, finden Sie diese hier im kompakten Ãœberblick und die Liste der gewährten Patente.
2012
Thomas Zink; Oliver Haase; Jürgen Wäsch; Marcel Waldvogel
P2P-RMI: Transparent Distribution of Remote Java Objects Journal Article
In: International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC), vol. 4, no. 5, pp. 17-34, 2012.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: Java RMI, NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer, Service Discovery | Links:
@article{Zink2012P2P-RMI,
title = {P2P-RMI: Transparent Distribution of Remote Java Objects},
author = {Thomas Zink and Oliver Haase and Jürgen Wäsch and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/zink2012p2p-rmi.pdf},
year = {2012},
date = {2012-09-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {International Journal of Computer Networks & Communications (IJCNC)},
volume = {4},
number = {5},
pages = {17-34},
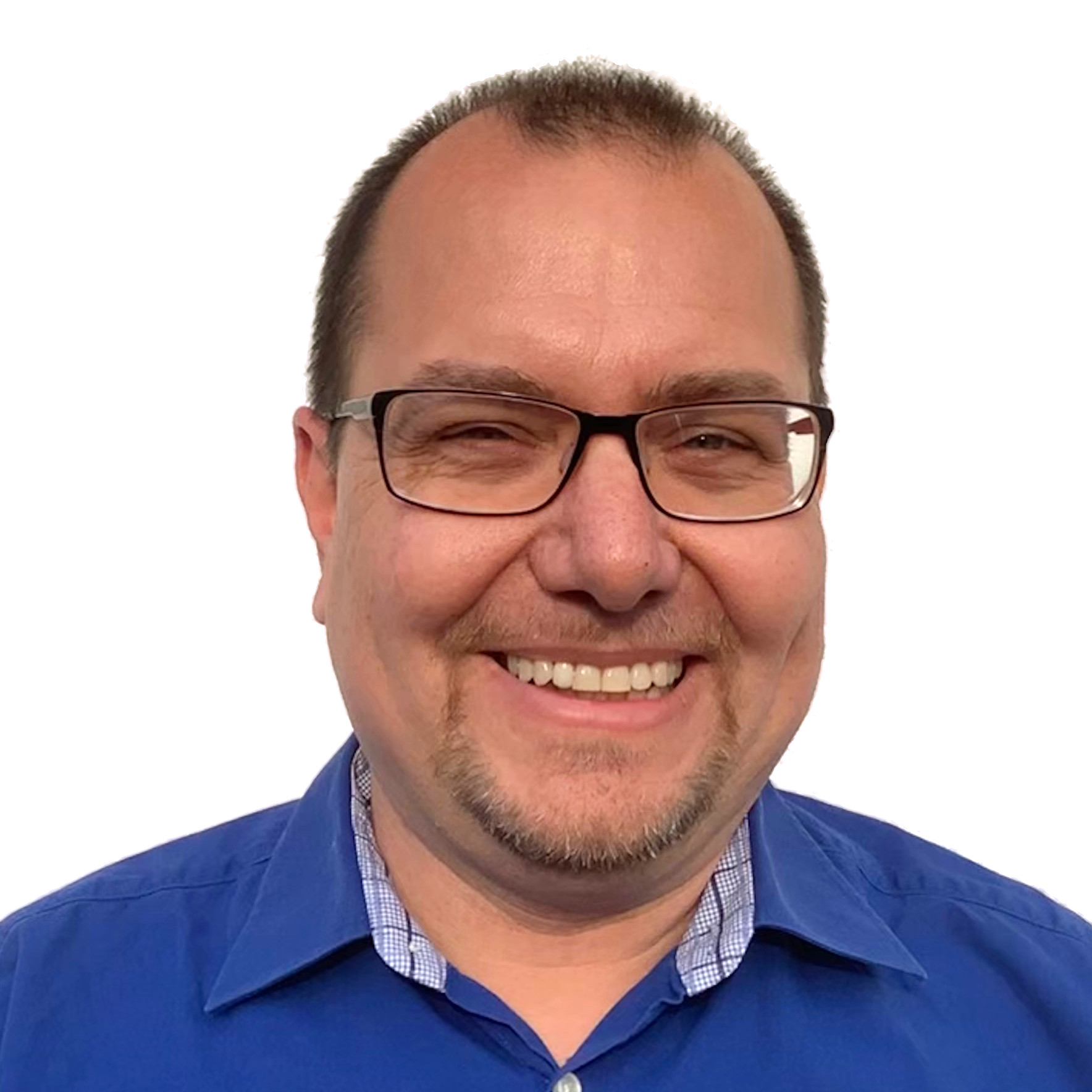
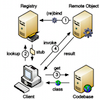
abstract = {Java Remote Method Invocation (RMI) is a built-in and easy-to-use framework for the distribution of remote Java objects. Its simplicity and seamless inter-virtual machine communication has made it a valuable tool for distributed services. It nevertheless exhibits certain constraints that practically limit RMI applications to the classical client/server distribution model, and make highly distributed and highly dynamic systems very difficult to build atop RMI.
We present an approach that makes Java RMI usable for P2P and similar distribution models. The solution basically consists of three ideas: (1) separate the location of the registry from the remote service object, (2) distribute the registry across a DHT infrastructure, and (3) transparently enhance the built-in communication between RMI servers and clients to allow traversal of NAT and firewall boundaries. Our approach is extremely lightweight, transparent, and requires practically zero configuration.},
keywords = {Java RMI, NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer, Service Discovery},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
We present an approach that makes Java RMI usable for P2P and similar distribution models. The solution basically consists of three ideas: (1) separate the location of the registry from the remote service object, (2) distribute the registry across a DHT infrastructure, and (3) transparently enhance the built-in communication between RMI servers and clients to allow traversal of NAT and firewall boundaries. Our approach is extremely lightweight, transparent, and requires practically zero configuration.
2011
Daniel Maier; Oliver Haase; Jürgen Wäsch; Marcel Waldvogel
A Comparative Analysis of NAT Hole Punching Journal Article
In: HTWG Forum, pp. 40-48, 2011, ISSN: 1619-9812.
BibTeX | Tags: NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@article{Maier2011Comparative,
title = {A Comparative Analysis of NAT Hole Punching},
author = {Daniel Maier and Oliver Haase and Jürgen Wäsch and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2011/maier11comparative.pdf},
issn = {1619-9812},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-11-01},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
journal = {HTWG Forum},
pages = {40-48},
keywords = {NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {article}
}
Daniel Maier; Oliver Haase; Jürgen Wäsch; Marcel Waldvogel
NAT Hole Punching Revisited Proceedings Article
In: Proceedings of IEEE LCN 2011, The 36th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks, 2011.
Abstract | BibTeX | Tags: NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer | Links:
@inproceedings{Maier2011NAT,
title = {NAT Hole Punching Revisited},
author = {Daniel Maier and Oliver Haase and Jürgen Wäsch and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2011/maier11nat.pdf},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-10-07},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of IEEE LCN 2011, The 36th IEEE Conference on Local Computer Networks},
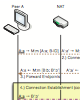
abstract = {Setting up connections to hosts behind Network Address Translation (NAT) equipment has last been the subject of research debates half a decade ago when NAT technology was still immature. This paper fills this gap and provides a solid comparison of two essential TCP hole punching approaches: sequential and parallel TCP hole punching. The comparison features current conditions and thoroughly compares setup delay, implementation complexity, resource usage, and effectuality of the two approaches. The result is a list of recommendations and a portable, effectual, and open-source Java implementation.},
keywords = {NAT traversal, Peer-to-Peer},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}
Weitere Informationen über mich finden Sie auf https://marcel-waldvogel.ch
