Links
Abstract
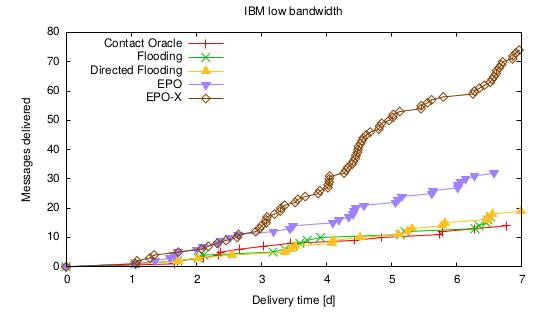
Routing in Opportunistic Networks, as a relatively young discipline, still lacks coherent, simple and valid benchmarks. It is customary to use epidemic routing as performance benchmark for Opportunistic Networks. We identify and describe the current simulation practices that do not expose the shortcomings of flooding as an upper bound. In this paper to provide a step towards a routing benchmark, which is flexible, provides results close to an upper bound, is simple to implement, and thus might be a candidate for a common benchmark. This new method called EPO, does not suffer from bottlenecks that limit the performance of epidemic flooding, even when bandwidth is scarce. Our analysis shows that networks are not suffering from that much severe congestion as suggested by flooding and thus giving a better insight to the underlying network.
BibTeX (Download)
@inproceedings{Islam2011Questioning,
title = {Questioning flooding as a routing benchmark in Opportunistic Networks},
author = {Arshad Islam and Marcel Waldvogel},
url = {https://netfuture.ch/wp-content/uploads/2011/islam11questioning.pdf},
year = {2011},
date = {2011-03-26},
urldate = {1000-01-01},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Baltic Congress on Future Internet Communications},
pages = {128-133},
abstract = {Routing in Opportunistic Networks, as a relatively young discipline, still lacks coherent, simple and valid benchmarks. It is customary to use epidemic routing as performance benchmark for Opportunistic Networks. We identify and describe the current simulation practices that do not expose the shortcomings of flooding as an upper bound. In this paper to provide a step towards a routing benchmark, which is flexible, provides results close to an upper bound, is simple to implement, and thus might be a candidate for a common benchmark. This new method called EPO, does not suffer from bottlenecks that limit the performance of epidemic flooding, even when bandwidth is scarce. Our analysis shows that networks are not suffering from that much severe congestion as suggested by flooding and thus giving a better insight to the underlying network.},
keywords = {Mobile Networks, Opportunistic Networks},
pubstate = {published},
tppubtype = {inproceedings}
}